ISO 9001:2015 Transition and Quality Management Strategies
Explore the transition to ISO 9001:2015, understand the key steps for success, and delve into decision-making principles for effective quality management. Learn how to address risks, make evidence-based decisions, and navigate the context of your organization to achieve strategic objectives efficiently.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
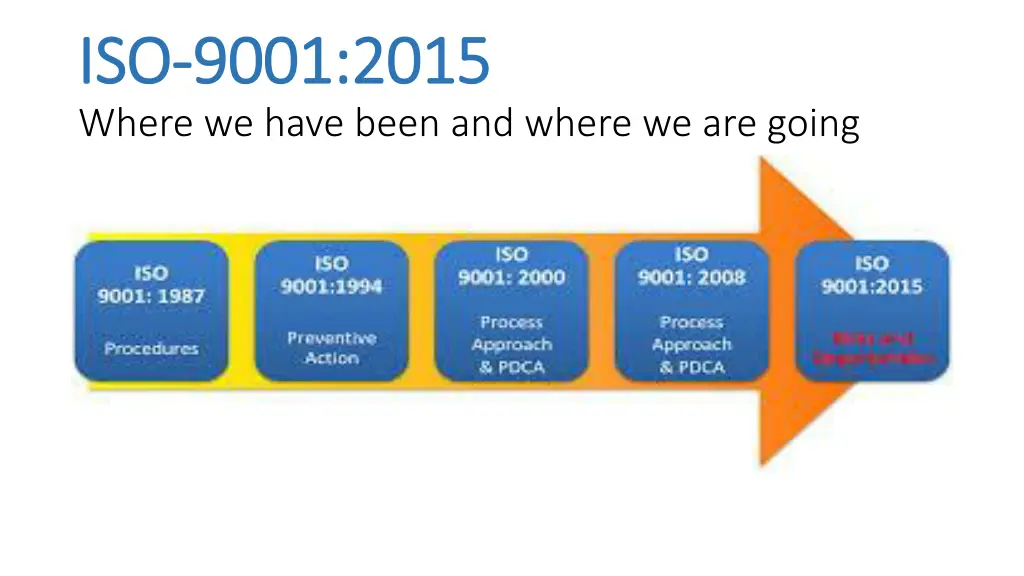
ISO ISO- -9001:2015 9001:2015 Where we have been and where we are going
Transition Transition Key to success Key to success 1) Understand the requirements 2) Conduct a gap analysis 3) Don t let concerns with auditability and documented information drive bureaucracy into your quality management system. 4) Implement changes that add maximum value to your organization.
Agenda Agenda Context of the Organization Process Approach and Risk Based Thinking
Context of the Organization Context of the Organization
Context of the Organization Context of the Organization The new requirement reads: The organization shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose and its strategic direction and that affect its ability to achieve the intended result(s) of its quality management system.
Decision making and ISO Decision making and ISO- -9001:2015 9001:2015 The first is a quality principle quoted from ISO 9000:2015, namely evidence- based decision making. It is not hard to understand that better decisions are made when they are based on evidence rather than by conjecture. The second is found in Clause 0.1, Addressing risks and opportunities associated with its context and objectives. Addressing risks means proactively managing uncertainties. The simple meaning of managing uncertainties is that decisions should be made with consideration of the possible positive and negative consequences that the uncertain future may bring. Finally, in Clause 5.1, entitled Leadership and Commitment, there is a requirement for top management: Ensuring that the quality policy and quality objectives are established for the quality management system and are compatible with the context and strategic direction of the organization. Top management s most basic role is strategic decision-making for the organization.
Decisions are to be made based on evidence. Evidence is found in the CONTEXT CONTEXT of the organization.
Internal Context Internal Context Vision Mission Strategic objectives and direction Organizational Chart SOPs Resources Culture
External Context External Context Legal Social Political Regulatory Financial Economic Market Trends
Examples Examples Customer pressures and complaints can force organizations to change policies such as product returns and customer and technical support . Technological changes can provide new and more effective ways to handle communications, operations, shipping and logistics. Governments regulatory and trade policies can play a significant role in determining how businesses operate, especially in regard to international trade, taxation, and regulations The media, including social media, can have a huge impact on a company s image and public relations. A bad news video or news report can go viral pretty fast, and if your organization doesn t provide an acceptable response, the negative publicity and effects can last a long time. Sociological forces often drive what, where and how consumers buy product and services. There is an increasing trend in the number of consumers purchasing products online and reading reviews before making a purchase. The multinational and multicultural trend in workforce composition can cause significant changes in hiring and retention of competent human resources.
Risk Based Thinking Risk Based Thinking Examples and Ideas Examples and Ideas Purchasing Design and Development Process
Purchasing Purchasing Supplier Approval and Re Supplier Approval and Re- -Evaluation Evaluation Do all raw materials create the same risk for your final product? Do all suppliers bring the same risk to your business? Does your current QMS account for these differences?
Design and Development Design and Development Design FMEA for actual design Risk Registers for project risks
The Process The Process A Approach and Risk pproach and Risk B Based ased T Thinking hinking Assign a Process Owner Define the process Identify the inputs and outputs Define measures of effectiveness and efficiency Identify risks and opportunities Report on the status of each process
Manpower (Training/Skills) Materials Measures RISK! Suppliers (By whom) Customer (For Whom) PROCESS Inputs Outputs Methods (How) Machine (With what) Environment (Conditions)
Process Definition Process Definition Should include: Process Owner, Inputs and Outputs, Process, Process Metrics and RISK
Process Review Process Review Should include: Inputs and Outputs, Process, Process Metrics and RISK
Process Owners Meetings Process Owner s Meetings Owner/Co-Owner Reporting Process Metrics Current State Recent Updates Plans moving forward Audit Nonconformance's (Internal and External) Dashboard RISK
Purchasing Purchasing Measurable: # Supplier Nonconformance's Process Owner: Goals 2016: 10% Reduction from 15 Risk: Production interruptions due to material shortages Risks and Opportunities: Supplier Nonconformances - 2015 90 80 Risk This rate of supplier rejects has resulted in 280 hours of line shut downs in 2015, and the trend is not improvement moving into 2016. 70 60 50 40 30 20 Opportunity: IF the shipping damage issues could be solved, we could eliminate 24 % of the nonconforamnces and 20% of the hours of line interruption 10 0 Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Series1 32 78 45 36 64 24 56 20 66 43 26 47 Corrective Action Plans: Task Supplier Nonconformances - 2015 Responsibility Target Date 250 200 150 100 50 0 Dimensional Damaged Functional Aesthetics Wrong Product
Quarterly Business Reviews Quarterly Business Reviews (Management Representative and Process Owners) Review of identified risk within each key process Has the risk changed? Have high risk issues been addressed? Does performance to objectives reflect risk mitigation?
Integrated Systems and RISK Integrated Systems and RISK ISO-9001 ISO-14000 FSSC- 22000, SQF, BRC (Food Standards)
Hazard Analysis for food safety Hazard Analysis for food safety Hazard Analysis - Food Safety (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) Is this hazard CONTROLLED or ELIMINATED (or reduced to an acceptable level) at a subsequent process step? If YES, this step is not a CCP. Identify the subsequent process step and proceed to the next process step. If the hazard is not controlled at this process step, go to column 10 and assign a CCP number. Does this process step INTRODUCE or INTENSIFY a potential food safety hazard? If YES identify the hazard(s). Assess probability, severity and risk per columns 4, 5 and 6. List the support programs that CONTROL or ELLIMINATE this hazard. Do the support program(s) control the hazard to an acceptable level? If yes, proceed to the next process step. If no, proceed to column 9. List each process step from the Process Flow Diagram Justification of Risk Level Assessment CCP or oPRP Process Step Likelihood Severity Risk Raw materials are received covered and/or packaged, Trailer Checks, Sealed Truck B- Pathogen contamination due to uncontrolled transportation Purchasing Program Shipping and Receiving Program L M 2 Yes No Raw materials are received covered and/or packaged, Trailer Checks, Sealed Truck Purchasing Program Shipping and Receiving program Chemical Control Program C- Chemical contamination due to uncontrolled transportation L M 2 Yes No Receive raw materials 1 Purchasing Program Shipping and Receiving Program Glass and Brittle Plastics Program Metal and Blade Control Program P- Physical contamination with extraneous material due to uncontrolled transpiration Raw materials are received covered and/or packaged, Trailer Checks, Sealed Truck L L 1 Yes No
ISO ISO- -14000 Aspects and Impacts 14000 Aspects and Impacts Aspect and Impacts Risk Assessment - ISO-14000 environmental aspect Other Requirements (Yes), (No) or (NA) Process Step Significant Likelihood legal and Severity Impact (Use notes to insert further analysis) Risk Aspects B - none NO NO Air Air Land Land Water Water Receiving C - none NO NO Air Air Land Land Water Water P- Potential for Scrap L L 2 NO NO Air Air Land Land Water Water
Quality Risk Assessment Quality Risk Assessment Risk Assessment - Quality (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Is this hazard CONTROLLED or ELIMINATED (or reduced to an acceptable level) at a subsequent process step? If YES, this step is not a QCP. Identify the subsequent process step and proceed to the next process step. If the risk is controlled at this process step, go to column 10 and assign a QCP number. (10) List the support programs that CONTROL or ELLIMINATE this risk. Do the support program(s) control the risk to an acceptable level? If yes, proceed to the next process step. If no, proceed to column 9. List each process step from the Process Flow Diagram Does this process step INTRODUCE or INTENSIFY a potential quality issue?Assess Likelihood and severity and risk per columns 4, 5 and 6. Process Step Likelihood Severity Justification of Risk Level Assessment Risk QCP Receive raw materials 1 Q - L M 2 No
What should you do? What should you do? Identify what the risks and opportunities are in your organization it depends on context Analyze and prioritize the risks and opportunities in your organization what is acceptable? what is unacceptable? Plan actions to address the risks how can I avoid or eliminate the risk? how can I mitigate the risk? Implement the plan take action Check the effectiveness of the actions does it work? Learn from experience continual improvement






















