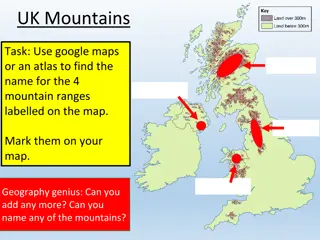
Journey Through Geology: Discovering Rock Types
Rocks are nature's masterpieces, each category unveiling a unique story of formation and significance. Explore the birth of minerals, the art of weathering, erosion's sculpting power, and more in this exciting geological journey. Gain insights into rock types, their environments, and their vital role in shaping landscapes. Embrace the Earth's wonders through the interconnected processes of rocks and their impact on our lives.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Understanding Rocks: Nature's Masterpieces A Journey Through Geology Photo by Pexels
01 Rock Categories Unveiled Table of Contents 02 The Birth of Minerals 03 The Art of Weathering 04 Erosion: The Sculptor of Landscapes 05 Mass Wasting: The Downhill Flow 06 Sedimentation: Nature's Layers 07 Interconnected Processes 08 The Importance of Rocks 09 Rocks in Our Lives 10 Conclusion: Embrace the Earth 11 Thank You!
1 Rock Categories Unveiled Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic Rocks are categorized into three main types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Each type has unique properties and formation processes. Igneous rocks form from cooled magma or lava, while sedimentary rocks are created from accumulated sediments. Metamorphic rocks result from transformation under pressure and heat. Understanding these types helps in recognizing their characteristics, uses, and significance in our world. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for exploring the intricate connections between rocks and their environments. Photo by Pexels
2 The Birth of Minerals Origin and Formation Common minerals originate from various geological processes, including crystallization from molten rock and precipitation from water. The environment of formation can range from deep within the Earth to surface conditions where evaporation plays a key role. Minerals like quartz and feldspar are abundant in igneous rocks, showcasing their origins in those fiery depths. Recognizing the formation environments of minerals provides insight into the rock types they compose. Photo by Pexels
3 The Art of Weathering Breaking Down Rocks Weathering is the process that breaks down rocks into smaller particles throughphysical, chemical, and biological means. These processes can be influenced by climate, topography, and the composition of the rocks themselves. Understanding weathering helps us grasp how landscapes evolve over time and the role of rocks in our ecosystem. This breakdown is crucial for soil formation and nutrient cycling essential for life. Photo by Pexels
4 Erosion: The Sculptor of Landscapes Movement of Materials Erosion is the movement of weathered rock and soil, shaped by wind, water, and ice over time. This natural sculpting transforms environments, creating features like valleys, canyons, and deltas. For example, river erosion can carve out deep gorges, showcasing the power of flowing water. Recognizing erosion s impact helps us appreciate the dynamic nature of our planet. Photo by Pexels
5 Mass Wasting: The Downhill Flow Gravity's Role Mass wasting refers to the movement of rock and soil down slopes due to gravity, often triggered by rainfall or an earthquake. Landslides, rockfalls, and slumps are examples of mass wasting that can reshape landscapes dramatically. Understanding mass wasting is vital for assessing hazards and planning land use in hilly regions. The effects of mass wasting can be both constructive and destructive, highlightingnature's duality. Photo by Pexels
6 Sedimentation: Nature's Layers The Build-up of Layers Sedimentation is the process of deposition where materials settle out of a transportmedium like water or air. This process creates layered deposits that can become sedimentary rocks over time through compaction and cementation. Recognizing sedimentary structures like fossils or ripples helps in understanding Earth's history. Sedimentary processes play a crucial role in resource formation and environmentalchanges. Photo by Pexels
7 Interconnected Processes The Rock Cycle All these processes weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation are interconnected within the rock cycle. Rocks are constantly transformed from one type to another over geological time, illustratingEarth's dynamic nature. This cycle emphasizes the relationship between surface processes and subterraneanformations. Understanding the rock cycle is essential for comprehending Earth's history and future changes. Photo by Pexels
8 The Importance of Rocks Beyond Beauty Rocks are not merely aesthetic; they serve critical functions in ecosystems, construction, and resource extraction. They influence soil formation, water quality, and habitat development for countless organisms. Rocks also provide materials for buildings, roads, and energy sources like fossil fuels. Highlighting their importance encourages stewardship and sustainable practices in geology. Photo by Pexels
9 Rocks in Our Lives Cultural and Practical Uses Throughout history, rocks have been integral to human civilization, from tools to monuments. They are used in art, architecture, and everyday items, showcasing their versatility beyond geology. Different cultures have unique relationships with local rocks, often integrating them into their identities. Understanding these connections enriches our appreciation of rocks in culture and utility. Photo by Pexels
10 Conclusion: Embrace the Earth Understanding Our Planet Recognizing the significance of rocks and their processes fosters a deeper connection with Earth. These geological marvels tell stories of our planet's history, evolution, and ongoing changes. By embracing geology, we can inspire future generations to appreciate and protect our natural world. Let s continue to explore and learn about these incredible gifts of nature. Photo by Pexels
11 Thank You! Questions and Discussion Thank you for joining this journey throughgeology and rocks. Feel free to ask questions or share insights from your own experiences with the naturalworld. Let s continue the conversation about the beauty and importance of our planet's geology. Together, we can inspire a greater appreciation for the Earth we inhabit. Photo by Pexels