Ketones: Boiling Points and IMF Differences
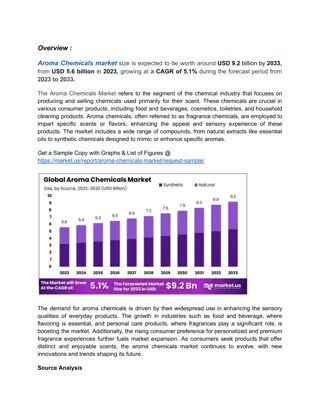
Learn about ketones, their properties, and the factors affecting their boiling points, such as intermolecular forces (IMF). Discover the polar nature of ketone molecules and how it influences their solubility in water, along with examples like acetone. Explore naming conventions for ketones and their common names like 2-propanone.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
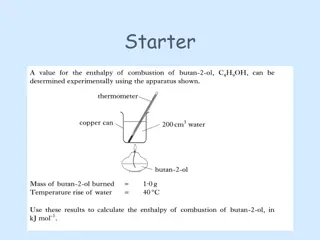
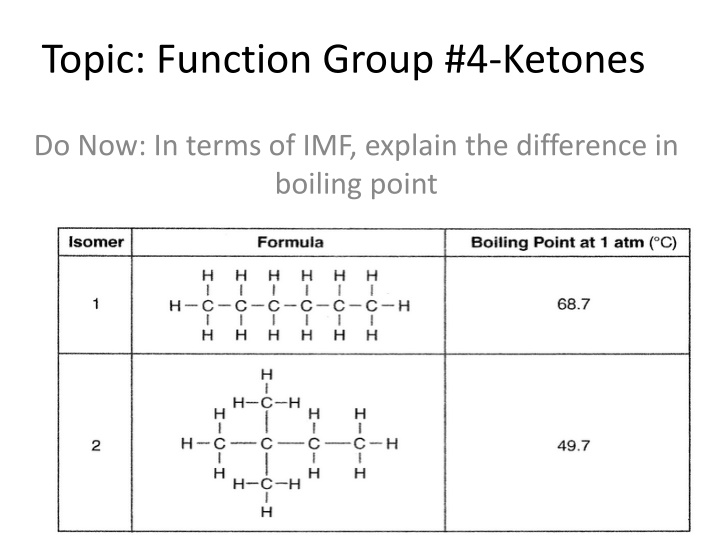
Topic: Function Group #4-Ketones Do Now: In terms of IMF, explain the difference in boiling point
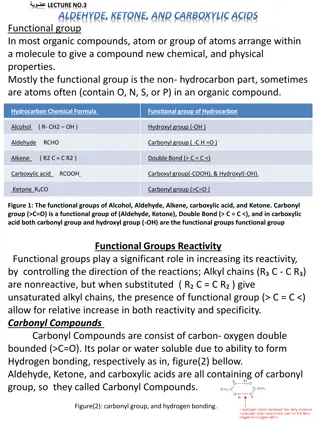
=O General Format: R C R' R and R' may or may not be the same (but have to be carbons/carbon chains) C =O Carbonyl group: located within C chain
Properties Carboxyl group makes ketone molecules polar = soluble in water Dipole-Dipole interactions Boiling point: higher than alkanes (same # C s) lower than alcohols (same # C s)
Have you ever smelled a ketone?! Camphor
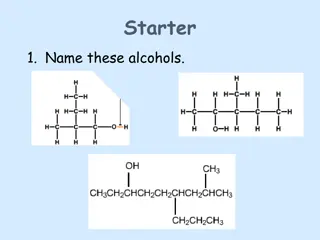
Naming Ketones Must use number to indicate location of carboxyl group use lowest possible number Take corresponding alkane name: Drop -e & add -one
2-propanone Common name = acetone 2-pentanone