Key Mathematical Concepts for Learning Success
"Explore a foundational curriculum covering topics such as rounding, algebraic notation, geometric properties, and statistical analysis to enhance mathematical proficiency. Develop a firm grasp of key mathematical principles through interactive learning modules."
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
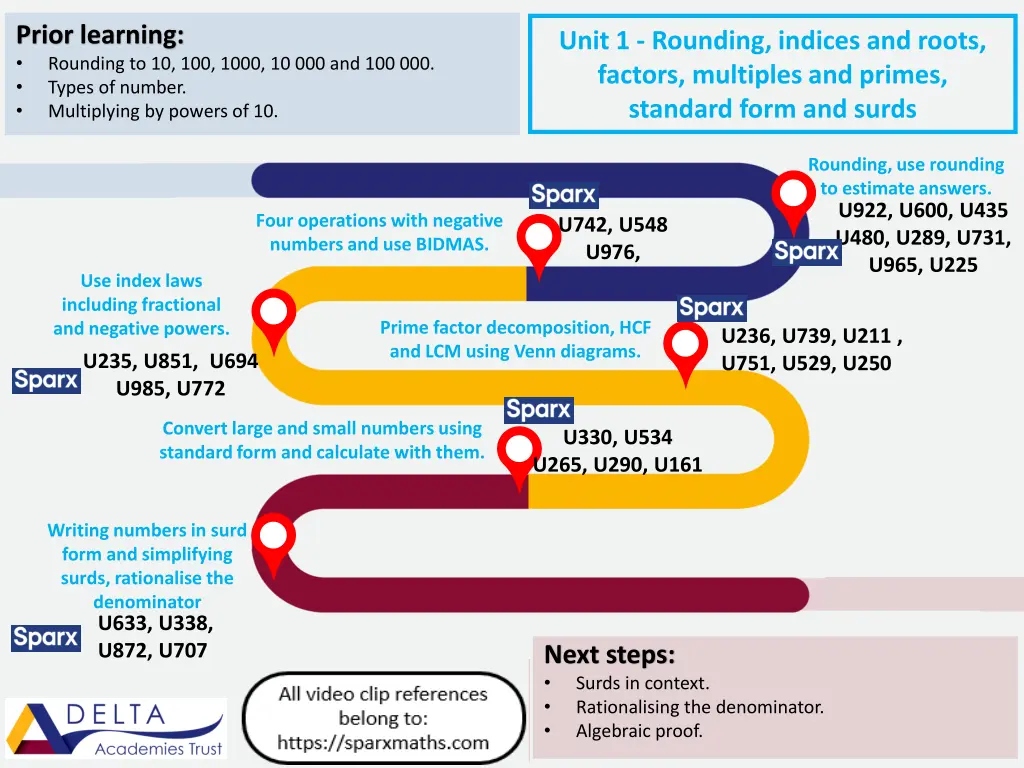
Prior learning: Rounding to 10, 100, 1000, 10 000 and 100 000. Types of number. Multiplying by powers of 10. Unit 1 - Rounding, indices and roots, factors, multiples and primes, standard form and surds Rounding, use rounding to estimate answers. U922, U600, U435 U480, U289, U731, U965, U225 Four operations with negative numbers and use BIDMAS. U742, U548 U976, Use index laws including fractional and negative powers. Prime factor decomposition, HCF and LCM using Venn diagrams. U236, U739, U211 , U751, U529, U250 U235, U851, U694 U985, U772 Convert large and small numbers using standard form and calculate with them. U330, U534 U265, U290, U161 Writing numbers in surd form and simplifying surds, rationalise the denominator U633, U338, U872, U707 Next steps: Surds in context. Rationalising the denominator. Algebraic proof.
Prior learning: Basic algebraic notation and symbols. Factors and multiples. Inverse operations. Order of operations (BIDMAS). Unit 2 - Like terms and substitution, Expanding, Factorising, Sequences Simplify algebraic expressions Select an expression/equation/for mula/identity from a list U613, U103 U613 Simplify algebraic expressions including fractional and surd coefficients. Substitution into expressions and formulae. U105, U662 U201 Expand and simplify expressions with single brackets Factorise into single and double brackets. U365 U179 Expand and simplify expressions with double brackets. Linear/quadratic/geometric and other sequences.U213, U530, U498, U768 U178, U963 U206, U958, U680 Factorise into double brackets Next steps: Algebraic proof. Solving algebraic fractions. Using algebra in context. Solving quadratic equations.
Prior learning: Addition and subtraction methods. Name 2D shapes. Using a protractor. Unit 3 - Properties of shapes, angles on parallel lines and within polygons Estimate, measure and draw angles U447 Angles on a straight line, in triangles, around a point and vertically opposite. U121, U390, U730, U628 Identify parallel lines and their angle facts. U826 Calculate angles in polygons. Solve problems with polygons U427 U427 Next steps: Similar triangles. Geometric proof. Transformations on a coordinate grid.
Prior learning: Calculating averages and range from lists of data. Simple frequency graphs and bar charts. Plotting coordinate points in the first quadrant. Unit 4 Averages and range, Comparison of distributions and stem-and-leaf diagrams Mean, median, mode and range revisited. Using the mean, median and mode work backwards U526 , U456 U260, U291 U717 Calculate mean, median, mode and range from a frequency table. U569 Compare two statistical Compare two statistical distributions distributions U569 Construct and interpret stem and leaf diagrams. U200, U909 Next steps: Interpretation and reasoning of statistical diagrams. Cumulative frequency, including inter-quartile range. Constructing and interpreting pie charts. Histograms
Prior learning: Place value. Percentage as an amount out of 100. Multiplication and division. Ordering integers on number lines. Unit 5 - Fractions, decimals and percentages Add and subtract decimals U478 Find fractions of an amount. U881 U916 Convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers. Multiply and divide decimals U293, U453, U868 U692 Four operations with mixed and improper fractions. U736, U793 U475, U544 Compare and order fractions. Calculate a percentage of an amount and express as percentage U554, U349, U925 U746 Percentage increase /decrease U773, U671 Percentage change and Reverse percentages. Convert between fractions, decimals and percentages and compare them. U888, U594 U278, U286 Convert fractions to recurring decimals. U689 Convert fractions to terminating decimals. U550 Next steps: Convert recurring decimals to fractions. Using ratio to divide amounts in context. Percentage profit and loss.
Prior learning: Division and multiplication methods. Identifying common factors. Simplifying and equivalent fractions. Unit 6 Ratio and proportion Simplify and compare ratios and write ratios as fractions. U687, U176 Share a quantity into a given ratio. U577 Write ratios in the form 1:n and n:1 U687 Solve problems using a unitary method. U753 Calculate the best value between products. U721 Use proportion with recipes. U721 Convert currencies using exchange rates. U610 Understand direct and inverse proportion. U640, U357 Next steps: Direct and inverse proportion (graphically). Solve problems in context using ratio.
Prior learning: Plotting coordinates in four quadrants. Substitution into formulae. Expanding brackets. Unit 7 Equations, Inequalities and Graphs Solving linear equations M175, M428 U755, U325, U870 Rearrange equations Construct and solve equations U599 U556 Represent and solve inequalities Plot coordinates and use in geometrical shapes U509 Find the coordinates of a midpoint U789, U889 U759, U738, U145, U337 U933 Plot and draw, or sketch linear functions in the form ? = ?? + ? Find the gradient of a line Length of a line segment U741 Identify and interpret equations of the form ? = ?? + ? U315, U669, Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines. U377, U898 U477 Next steps: Solve simultaneous equations graphically including linear, quadratic and circle graphs. Graphs of trigonometric functions. Transformations of graphs.
Prior learning: Recall square numbers from 1 1 up to 15 15. Indices and roots with the use of a calculator. Rearranging formulae. Unit 8 - Pythagoras theorem and Trigonometry (SOH CAH TOA) Calculate the length of a hypotenuse using Pythagoras Theorem. Calculate the length of a shorter side using Pythagoras Theorem. U385 U385 Use trigonometric ratios to find angles and lengths in 2D. Apply Pythagoras theorem to a line on a coordinate grid. U385 U605,U283, U545 Calculate angles of elevation and depression. U967 Know exact values for particular trigonometric ratios. U627, 319 Next steps: Apply Pythagoras theorem and simple trigonometry (SOH CAH TOA) in real life context. and within compound 2D shapes. Pythagoras and Trigonometry in 3D
Prior learning: Reading scales on a coordinate axes. Coordinates in four quadrants including direction. Equations of horizontal and vertical lines. Unit 9 Transformations, Constructions, Loci and bearings Recognise and describe reflections. Translate a shape by a column vector. U799 U196 Describe and draw rotations. U696 Describe and transform shapes using enlargements by a positive, fractional or negative scale factor. U519, U134 Describe and transform using combined transformations. Describe and draw front and side elevations and plans. U743 Use and interpret maps and scale drawings. U766 U257 Loci Constructions. U678, U187 U787, U245 U820 Understand, draw and measure bearings. U525 Next steps: Similarity and congruence. Column vector arithmetic. Transformations of curves.