Kinetic Theory of Matter & Its Effects on States of Matter
Learn about the kinetic theory of matter, which explains the constant motion of particles in solids, liquids, and gases. Explore how temperature and pressure impact the state of matter, including changes from solid to liquid to gas. Discover the relationship between temperature, pressure, and the volume of gases, as well as the process of diffusion in different concentrations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The kinetic theory of matter (particle theory) consists of many, very small particles which are constantly moving or in a continual state of motion. The degree to which the particles move is determined kinetic theory of matter (particle theory) says that all of many, very small particles which are constantly moving or in a The consists continual state of motion by the amount of energy they have and their relationship to other particles. The molecules in gaseous the highest to the particle s MOTION), and solid state energy. all matter matter gaseous state state have highest kinetic energy (energy due solid- - state molecules have the least least kinetic
What is the effect of on What is the effect of Temperature / Pressure on states of matter Temperature / Pressure states of matter? ? As the temperature of a solid, liquid or gas increases, the particles move more rapidly. As the temperature falls, the particles slow down. If a liquid s temperature is reduced i.e. if it is cooled sufficiently, it forms a solid. If a liquid s temperature is increased, if it is heated sufficiently, it forms a gas. What is the effect of pressure on states of matter? if pressure is increased on a substance its state changes from: Gas Liquid Solid Gas Liquid Solid.
How gas? How do temperature and pressure affect the volume of a gas? do temperature and pressure affect the volume of a The volume of a given gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure (Charles's law). inversely proportional to its pressure in constant temperature. (Boyle's (Charles's law). The volume of a given amount of gas is (Boyle's law law). ). Boyle's Law states that the volume the applied pressure volume of a given amount of gas is pressure when the temperature and mass are constant is inversely inversely proportional proportional with the temperature and mass are constant. Charles's law states that the volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to its temperature on the kelvin scale when the pressure is held constant directly proportional to its temperature on the kelvin scale when the pressure is held constant.
DIFFUSION DIFFUSION Diffusion concentration to an area of lower concentration gases when their particles collide randomly and spread out. Diffusion is also an important process for living things - it is how substances like oxygen, food or waste particles etc. move in and out of cells. Diffusion is concentration to an area of lower concentration . Diffusion occurs in liquids and is the movement of a substance from an area of high the movement of a substance from an area of high Diffusion in solids is a very slow process because the density of solids is very high as compared to liquid and gases. Hence, diffusion in solids is considered negligible. diffusion in solids is considered negligible. Diffusion in fluids slower than that in gases. This is because in gases, the particles spread quicker than liquids and fill the space available to them. Diffusion in fluids (liquids and gases) : The rate of diffusion in liquids is much Examples of -A tea bag immersed in a cup of hot water will diffuse into the water and change its color. -A spray of perfume or room freshener will get diffused into the air by which we can sense the odor. Examples of Diffusion: Diffusion:
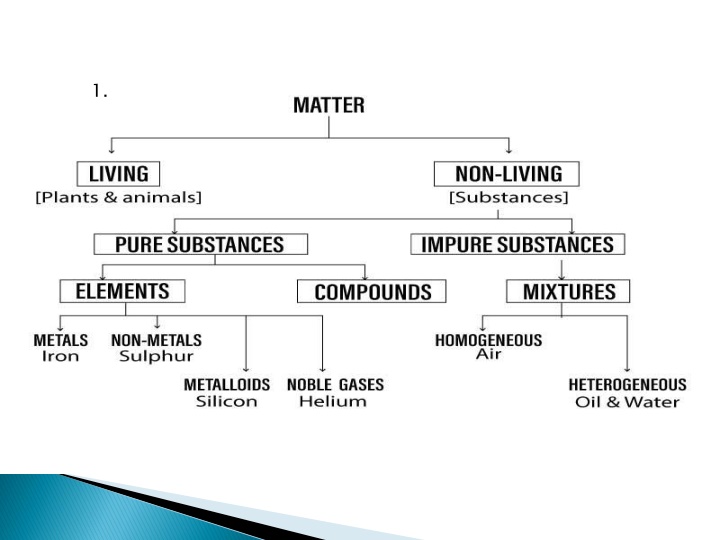
HW: HW:- - Find the Meanings of the following KEY WORDS KEY WORDS: 1. Ions 2. Noble Gases 3. Metalloids 4. Homogenous 5. Heterogeneous 6. Absolute temperature 7. Kinetic Energy 8. Pressure 9. Fluids
