Learning: A Two-Prong Approach
Explore the factors influencing learning, including affect, cognition, motivation, interest, emotional connections, self-regulation, and more. Delve into student experiences, varying affective responses, and strategies for successful learning outcomes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
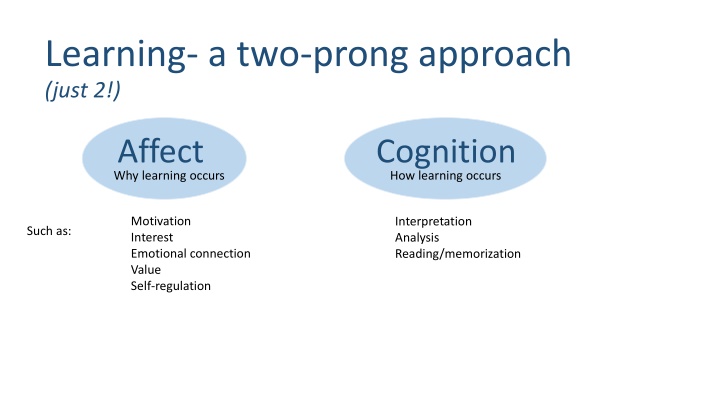
Learning- a two-prong approach (just 2!) Why learning occurs Affect Cognition How learning occurs Motivation Interest Emotional connection Value Self-regulation Interpretation Analysis Reading/memorization Such as:
Learning- a two-prong approach Affect Why learning occurs Motivation- student believes they can succeed Interest- a predisposition to engage with material (personal = triggered by personal experience or situational = triggered by novelty/competition) Emotionalconnection material address social goals or values Value - the topic is related to their own lives and/or interests? Self-regulation -monitoring and reflecting on one's learning strategies and their effectiveness and adjusting accordingly
Learning- a two-prong approach McConnell & van Der Hoeven Kraft 2011: Take-aways on student affect? Affect Why learning occurs Recall 3 student pairs (p 107) who had varying levels of affective experiences Motivation Interest Emotion Value Self-regulation Cathy & Megan (definitions) Ron & Dexter (summarize the chapter) Karl & Jen (chose the assignment on active volcanoes)
Learning- a two-prong approach Read two students learning experience (Monica & Emilie) Affect Why learning occurs Discuss specific examples of each students practice that results in more or less success Why do those actions matter? Motivation Interest Emotion Value Self-regulation Consider the metacognitive and motivational factors that influence each student s engagement. Who will be more successful on the exam?
Learning- a two-prong approach Read two students learning experience (Monica & Emilie) Affect Why learning occurs Novice Expert Expert Learner: Sets goals; plans studying with logistical constraints in mind; Identifies and uses strengths; Makes adjustments as needed; Usually happy with results, or adjusts Novice Learner: No plan (or poor plan) for studying, Uses limited methods; Poor recognition of her learning goals; Often disappointed with the results but doesn t know how to change things Motivation Interest Emotion Value Self-regulation = Metacognition
From Thursday: Review research on learning (NAP) Key findings Students come in to our classes with preconceptions, not blank slates Students must have the opportunity to develop a conceptual framework that facilitates retrieval and builds on deep knowledge A metacognitive approach helps students monitor their own learning and become better learners Promising practices: Developing (and using) learning outcomes Engaging students in activities during class, in groups Organizing content in scenarios, with context Getting and giving feedback through formative assessment
Metacognition: What is it and how do I do it? meta cognition
Metacognition Metacognition = = Thinking about thinking Learning about how people learn Developing an awareness of one s own learning process Monitoring and assessing one s own learning Making adjustments to one s learning process Managing one s motivation and attitudes
What can you do to support students metacognition? Provide opportunities for students to self-evaluate their own learning Establish an environment that fosters learning how to learn (modeling!) Encourage behaviors that foster learning to learn Low effort (activity-level): Moderate effort (activity/unit-level): Committed effort (course level): Learning journal Think-Pair-Share Reflective Prompts Reflective questions Exam Wrappers
Creating an environment that fosters learning to learn (intrinsic) Reward effort over ability (allow for revisions; participation instead of graded) Encourage self-comparison over social comparison (exam wrappers) Model and provide graphic organizers and other organizational structures Be explicit: spend time discussing how these activities help learning
Encourage behaviors that foster learning to learn (intrinsic) Encourage questioning and help-seeking Frequent use of think-pair-share Frequent use of reflective questions Encourage goal-setting Exam or module wrappers Course journals Be explicit: spend time discussing how these activities help learning
What activities have we explored that addressed metacognition and the affect component of learning? What could you do in your Large lecture course? Small -moderate sized lecture course? Lab section?





