Learning Looping Structures in Programming
This overview covers the fundamentals of looping structures in programming, specifically focusing on while loops and for loops. Understand the syntax, examples, and notes related to while loops, including how to avoid infinite loops and practical applications like computing factorial using a while loop.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Loops CMSC 201
Overview Today we will learn about: Looping Structures While loops For Loops
Looping Loops let us do something until a boolean condition is met. The simplest loop is called a while loop.
The while loop The syntax for a while loop is as follows: line-1 while someCondition: line-2 line-3 line-4
The while loop line-1 while someCondition: line-2 line-3 line-4 Condition is true Condition is false Condition is true line-2 line-3 line-1 line-4 Condition is false
Example a = 5 while a > 0: print(a) a = a 1 Prints 5 4 3 2 1
Notes If the condition is false to begin with, the loop never executes! a = 4 b = 5 while a == b: print( Hello ) print( Goodbye ) This will only print goodbye.
Notes It is very important that the variable in the condition be altered at some point during the loop. a = 5 while a > 0: print(a) This is called an infinite loop, since a will always be greater than zero.
Example Computing factorial with a while loop. findFac = input( Please enter a number ) currentTotal = 1 while findFac> 0: currentTotal = currentTotal * findFac findFac = findFac 1 print(findFac)
Example Let s examine this: findFac = input( Please enter a number ) currentTotal = 1 while findFac> 0: currentTotal = currentTotal * findFac findFac = findFac 1 print(findFac) The things in blue are our loop variables. These keep track of where we are and what we need to be doing.
Example Let s examine this: findFac = input( Please enter a number ) currentTotal = 1 while findFac> 0: currentTotal = currentTotal * findFac findFac = findFac 1 print(findFac) currentTotal stores our information, making sure we remember what our current working total is.
Exercise Use a while loop to print out every number between 0 and 100 that is divisible by three.
Loops + If Statements Now that you know how to use loops, if statements, and variables, you can create fairly complicated algorithms. However, figuring out how to combine them can be difficult! In the next few homeworks and exercises, you will start needing to figure out when to use each tool you ve been given so far. These are the basic elements of programming!
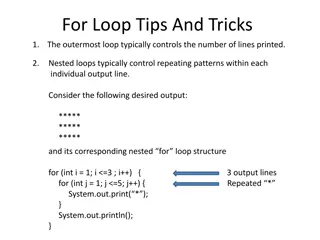
Nested Loops We can put loops in our loops. This is called nested loops. The first loop is the outer one is the inner inner loop. The inner loop can be executed many times. What does this loop print? outer loop, and the second a = 0 b = 0 while a < 4: while b < 4: print(b) b = b + 1 a = a + 1 b = 0