Light: Reflection, Refraction, and Interference in Optics
Explore the fascinating world of optics with topics ranging from the principles of reflection and refraction to the intricate phenomenon of interference. Delve into the concepts of index of refraction, chromatic dispersion, rainbows, and more. Discover the secrets behind the blue-green color of a Morpho's wing and the shifting colors of inks. Uncover the principles of Huygens and the laws of refraction, all illustrated with captivating images.
Uploaded on Aug 14, 2024 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sections 1. (reflection) (refraction) 2. (interference) 3. (diffraction)
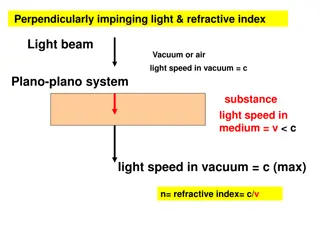
11-1 Reflection and Refraction ( ) 1 1 n n = = (reflectio n) sin sin (refractio n) 2 2 1 1
Chromatic Dispersion prisms and gratings
11-2 Interference () What produces the blue-green of a Morpho s wing? How do colorshifting inks shift colors?
Huygens principle All points on a wavefront serve as point sources of spherical secondary wavelets. After a time t, the new position of the wavefront will be that of a surface tangent to these secondary wavelets. Fig. 35- 2
Law of Refraction from Huygens principle
Fig. 35-3 10 35-
v v = = = = t t 1 2 1 1 ec hg v v 1 2 2 2 = sin (for triangle hce) 1 1 hc = sin (for triangle hcg) 2 2 hc sin sin v v c v = = = 1 1 1 n Index of Refraction: 2 c v 2 2 c v = = and n n 1 2 1 2 sin sin c n c n n n = = 1 1 2 = sin sin n n Law of Refraction: 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 11 35-
Phase Difference, Wavelength and Index of Refraction
Wavelength and Index of Refraction v c v c = = = n n n n v c n c = = = = f f n n n The frequency of light in a medium is the same as it is in vacuum 35- 13
Phase Difference Since wavelengths in n1 and n2 are different, the two beams may no longer be in phase Fig. 35-4 L L Ln Ln = = = Number of wavelengths in : 1 n N 1 1 n L 1 1 n L = = = Number of wavelengths in : 2 n N 2 2 n 2 2 n Ln Ln L ( ) = = Assuming : 2 2 n n N N n n 2 1 2 1 2 1 = 1/2 wavelength destructive interference N N 2 1 35- 14
Ex.11-1 35-1 wavelength 550.0 nm n2=1.600 and L = 2.600 m