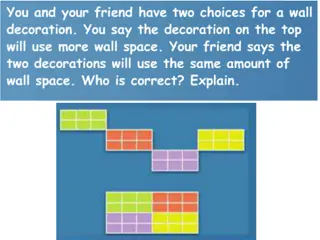
Linguistic and Cultural Study Insights
Explore the intersection of language and culture through lingvoculturology, analyzing how language shapes perceptions and reflects cultural nuances. The study delves into the evolution, comparison, and contrast of language within various social groups and ethnicities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lingvoculturology a relevant research area? Claus Mathiesen Institute of Foreign Languages Royal Danish Defence College
From Chomsky to Humboldt universalism people might speak differently, but they think more or less in the same way humboldtianism that people speak differently, depicts the fact, that they think differently, and thus , have a different perception of the surrounding world
Culture and Civilisation Culture develops in to main directions: to cover the material needs of the human being -> civilisation to cover the spiritual needs of the human being -> culture having a symbolic nature To our issue, lingvoculturology , culture is of more importance than civilisation
Language Every new bearer of a language creates his vision of the world NOT based on an independent arranging of his of his own thoughts and impressions, but in the framework of the experience of his ancestors, embedded in the meanings of the language. At the same time, language is a mean of discovering things, which are not yet discovered. Language not only gives names to things in a culture, but also developes within the culture.
Language and culture Language is a precondition of culture a foundation of culture a product of culture Heidegger: language is the home of human existence the studie of language is a strategic science
Lingvoculturology the idea of studying the culture through the language is not a new one lingustics - lingvoculturology - culturology lingvoculturology = the studie af the traces of culture in a given language
Lingvoculturology 5 main directions descriptive: a social group, an etnic group, a people etc. diachronic: registering changes in a group over a time period comparative: two or several groups, peoples contrastive: contrasting two (or more) groups to reveal important differencies leksiko-graphic: developing dictionaries of significant words an expressions used in a group
Why is lingvoculturology so important? tools to breaking the cultural barriers WHAT to say and, most importantly, WHEN and HOW to say it? necessary, when doing translations and interpretation ought to be an important feature in language training
The objects of lingvoculturology Specific language units ( deposits of culture ) in: rituals, customs and manners theory, that language developed in connection with rituals and rites myths and legends (archetypes) folklore poetry and prose symbols proverbs, idioms and phrases (specific for a group, not common, for example from the Bible) comparisons metaphores styles and inventory of styles etiquette nonequivalent vocabulary lacunas (lexical gaps)
Text, language and culture all texts are to be seen as products of a given language and a given culture at the same time very often, the specific cultural information is based on associations, that is, at the very peryphery of meaning these elements of meaning are often related to the system of values of a given group (people)
Sapir/Whorf: human beings see/experience reality through their language, that means, differently Language Picture of the world shaped by language Objective reality ?