Lymphatic System
Explore the formation of tissue fluid, lymphatic system function, and the role of blood proteins in maintaining fluid balance and fighting infections. Learn about the structure and role of the lymphatic system in transporting lymph throughout the body to combat infection. Discover how hydrostatic pressure drives blood out of capillaries, aiding in the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Formation of tissue fluid and lymph Key terms: Tissue are cells that share a similar structure working together to form a structure Tissue fluid Fluid from the capillaries that surrounds the tissue Lymph maintains fluid balance in cells and removes bacteria
Formation of tissue fluid and lymph By the time blood reaches the capillary beds from an artery, it is at high pressure and this forces blood plasma out. The plasma leaves the capillary and becomes tissue fluid. As the blood plasma moves through the capillary bed towards the vein, pressure drops and stops plasma being squeezed out This allow for diffusion and the exchange of oxygen and waste products from cells (http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/triple_ocr_21c/further_biology/c irculation/revision/4/)
(http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/triple_ocr_21c/further_biolog(http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/triple_ocr_21c/further_biolog y/circulation/revision/4/)
Role of hydrostatic pressure This is the force between the capillaries and tissues, driving the blood out of the capillaries as it is greater than the external pressure, in order for the exchange of oxygen and glucose for waste products from the cells known as osmosis
Blood Proteins There are 3 proteins within blood that all have different roles: Albumin made by the liver and is responsible for keeping the fluid pressure level constant and carrying nutrients and vitamins to where they are needed in the body Globulin provide antibodies so that the body can fight off infection Fibrinogen made by the liver to work with platelets and create blood clots
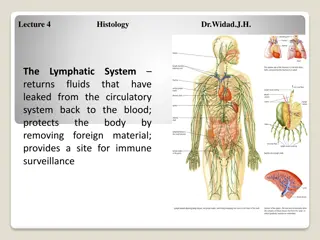
Structure and role of lymphatic system https://www.livescience.com/26983-lymphatic- system.html - video 2 mins The lymphatic system is consists of tissues and organs that help rid the body of unwanted materials such as toxins. The main function of the system is to transport lymph, containing white blood cells, throughout the body in order to fight infection. The system consists of vessels which are similar to blood vessels, these are connected to your lymph nodes (which become swollen when fighting infection) and the lymph is filtered Your tonsils, adenoids and spleen thymus are all part of the system