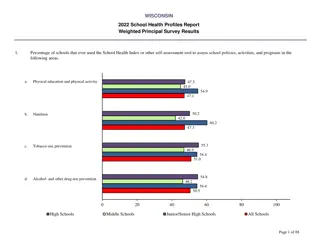
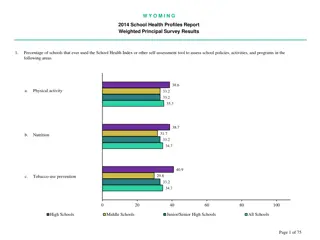
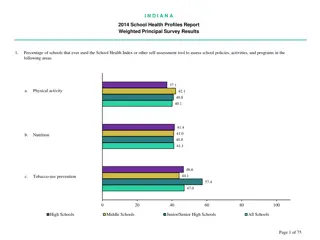
Managing Health and Safety in School Productions
In a school setting, it is crucial to prioritize health and safety during productions. Understanding key duties under the Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 is essential for effectively managing risks and ensuring a safe environment for all involved. Learn how to implement policies, consult with relevant parties, and apply learnings through case studies to prevent harm and promote a culture of safety in performing arts activities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Health and Safety In Performing Arts For Schools August 2017
Workshop Outcomes We want you to understand: Why We Need to Manage Health and Safety in Our Productions Some Key Duties Under The Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 How to Manage Health and Safety In Productions or Events Managing Health and Safety for Productions and Events Policy Developed by St Kentigern Initiation Planning Implementation Closure Apply Our Learning Through Case study
We want to prevent harm to our charges We want to ensure lessons are learned
Duty Holders Under the HSW Act PCBU Worker Others Officer
Person Conducting a Business or Undertaking (PCBU) Is the organisation that Has the primary duty of care for workplace health and safety Duty to manage risks Replaces current duties of employers, principals and persons in control of a place of work Responsible for "workers" and "others affected by the work". Duty to Consult, Communicate, and Co-ordinate Activity with other PCBU s Duty of care extends beyond employees
Reasonably Practicable - Considerations Knowledge of Harm Degree of harm Likelihood Knowledge of Controls Cost grossly disproportionate
Not All Controls Are Equal Eliminate Substitute Collective protection Isolate Engineered controls Individual protection Administrative controls Personal Protective Equipment
The St Kentigern Health and Safety in Performing Arts Policy
Managing Health and Safety for Productions and Events Reflects best practice: A Guide for Safe Working Practices in the New Zealand Theatre and Entertainment Industry (ETNZ, https://www.etnz.org/) Safety Guidelines for the Entertainment Industry (Australian Entertainment Industry Association and the Media Entertainment and Arts Alliance)
Managing Health and Safety for Productions and Events It views a production terms of four key phases: 1. Initiation 2. Planning 3. Implementation 4. Closure
Initiation Key Points The organisers must scope out the production This must include a high level screen of critical hazards and associated risks Are there any showstoppers or things the Board of Trustees need to know about? What is required to run it safely? Approval of concept and approach is required
Planning Key Points Design in health and safety Must define clear roles and lines of responsibility Must identify, assess and develop controls for the critical hazards and associated risks (RAMS). Must use layers of control All key health and safety information (e.g. risk assessments, responsibilities, management of third parties etc) should be included in a health and safety plan for the production (Production Plan).
Critical Hazards and Associated Risks Set Construction Work at Height Working in Confined Spaces Exposure to Lighting Ergonomic Hazards Plant and Equipment Biological Hazards Exposure to Noise, Hazardous Sequences, Props and Substances Exposure to Stress and Fatigue Outdoor Performances and Events.
Key Attributes of the Producer Must be proactive and deliberate in approach to H&S Must be risk aware (but remember we are not trying to remove all risk) Must focus on Critical Hazards and Associated Risks . Don t reinvent wheels Must remember it is easy to become complacent
Implementation Key Points Typically three areas: Set Build, Rehearsal, Live Production Verify capability/competency of all third parties (contractors, volunteers) Manage conflicting work activity Implement the health and safety plan (Production Plan) update as required Monitor all activity Communicate, Communicate, Communicate
Key Attributes of the Producer Must be an H&S Leader Must be watchful, attentive, and open to issues Must engage with everyone Must be aware of the key risk factors for their people fatigue, time pressure, conflicting work
Closure Key Points There are two elements within closure: 1. Decommissioning of the production This is a high risk period people can be tired and distracted Same H&S requirements as for implementation 2. Capturing lessons learned Debriefing session/s Record, communicate, apply next time
Key Points Reflect on introduction and key outcomes What are the key takeaways?