Manitoba Non-Profit Housing Association Audit Overview
Learn about the difference between accounting and auditing, the purpose of audits, what an audit is not, materiality in auditing, and the concept of audit sampling.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Manitoba Non-Profit Housing Association What is an audit Derrick Vandel| CPA | CA
Accounting and Auditing What is the difference between accounting and auditing? Accounting is the recording and classifying of transactions and balances from supporting documents by an organization in order to produce a set of financial statements. Auditing is the examination and verification of an organization s financial and accounting records and supporting documents by a third party chartered accounting firm such as The Exchange Group to ensure the financial statements are not materially misstated, and are presented in accordance with Canadian Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Why do We Perform Audits? To ensure that assets (Items owned by or owed to the organization) and liabilities (Items owed by the organization) exist and are fully recorded and disclosed in accordance with GAAP. To ensure that all revenues and expenses of the organization are properly recorded in accordance with GAAP. To ensure Note disclosures in the financial statements meet GAAP requirements
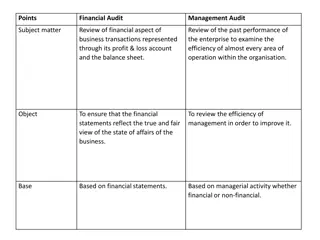
An Audit is NOT: Assurance as to future viability An opinion as to how efficient or effective an organization was An opinion as to how well internal controls operated Bookkeeping
An Audit is NOT: An audit is not intended to find fraud. The auditor does not specifically look for fraud. Transaction testing and analytical review performed by the Auditor may uncover fraud.
Materiality Materiality is defined as the amount a set of financial statements could be misstated before someone who is using them would change their opinion of an organizations operations. All audits are performed with Materiality in mind. Materiality levels are determined by the auditor using professional judgement based on knowledge of who the users of the financial statements will be. Materiality for Not-for-Profit organizations is typically based on 1% - 3% of expenses.
Audit Sampling Auditors do not review supporting documentation for every transaction. Auditors choose a sample of items recorded in the general ledger. This sample is based on professional judgement of the risks within certain areas of the records Based on this sample, the auditor will decide whether the financial statements are materially stated.
Auditors Report and Opinion Unqualified Opinion: An opinion is said to be unqualified when the Auditor concludes that the Financial Statements give a true and fair view in accordance with the financial reporting framework used for the preparation and presentation of the Financial Statements. An Auditor gives a Clean opinion or Unqualified Opinion when he or she does not have any significant reservation in respect of matters contained in the Financial Statements.
Standard Audit Report Please refer to Handout example
Auditors Report and Opinion Qualified Opinion: is given by the auditor in either of these two cases: 1. When the financial statements are materially misstated due to misstatement in one particular account balance, class of transaction or disclosure that does not have pervasive effect on the financial statements. 2. When the auditor is unable to obtain audit evidence regarding particular account balance, class of transaction or disclosure that does not have pervasive effect on the financial statements. Example: The Organization had recorded a receivable in the amount of $2,000 from a tenant in arrears . We could not obtain sufficient audit evidence to support the receivable.
Auditors Report and Opinion Disclaimer of Opinionis issued in either of the following cases: 1. When the auditor is not independent or when there is conflict of interest. 2. When a scope limitation is imposed by the client, which results in the auditor being unable to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence. 3. When the circumstances indicate substantial problem of going concern in client. 4. When there are significant uncertainties in the business of client. 5. When the balances and transactions recorded by an organization cannot be audited. This opinion is usually given due missing documentation or due to lack of organization of books and records.
Finance Policies and Procedures Finance Policies and Procedures of an organization are the written documentation as to what each person does and how they do it. Examples of Policies and Procedures include: Obtaining written approval before making a purchase Entering an invoice into the computer system and then signing an initial on the invoice as proof that it was entered Printing a cheque, and submitting the cheque to someone else with signing authority to sign the cheque
Manitoba Non-Profit Housing Association What is an audit? Derrick Vandel| CPA | CA