Marketing Environment Forces
The marketing environment encompasses both macro and micro forces that influence a company's ability to connect with its target customers. Explore the impact of environmental, societal, and internal factors on marketing strategies, highlighting key stakeholders, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats faced by businesses. Delve into concepts like Porter's 5 Forces and examine how businesses navigate challenges and seize opportunities in dynamic markets.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Definition The actors and forces outside marketing that affect marketing mgt s ability to build and maintain successful relationships with target customers Kotler Today's marketers need to adopt their strategies and to meet new challenges and opportunities markets change rapidly and
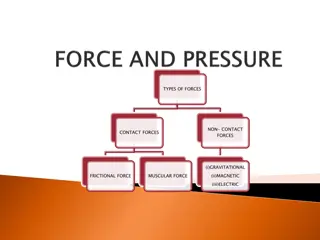
The Environmental forces Marketing Environment -Macro- Legal factors Technological factors Marketing Environment -Micro- PESTLE PESTLE Consumer The Internal Environment COMPANY Supplier Political factors Economic factors Stakeholder Environmental factors Socio- Cultural factors The Marketing Environment
Micro Environment The actors close to the company that affect its ability to serve its customers Macro Environment The larger societal forces that affect the micro environment
Exercise :Internal Environment Men Money Material Machinery Markets (Analyzing in the context of Sri Lankan Airlines)
Micro Environment- Key Stakeholders Suppliers Pressure groups Competitors Company Employees & Unions Customers Channel Partners (Intermediaries) Share holders & creditors
Strengths Weakness Brand Product portfolio Financial Resources Managerial ability Knowledge/Skill Economies of scale Technology Lack of skilled labor High labor turn over Overcapacity Poor internal communication Supplier relationships Opportunity Threats Investments Diversifying portfolio Global markets Internet Innovation Demand for high quality products Competitor activity Supplier desertion Market saturation Substitute products Resistance to change
Porters 5 Forces Potential Entrant (Threat of Mobility) Industry Rivalry Supplier Buyer (Supplier Power) (Buyer Power) Substitutes (Threat of Substitutes)
Industry Rivalry Sustainable competitive advantage through innovation Competition between online and offline companies Level of advertising expense Powerful competitive strategy Apple vs Anroid
Bargaining Power of Suppliers Supplier switching costs relative to firm switching costs Degree of differentiation of inputs Impact of inputs on cost or differentiation Presence of substitute inputs Strength of distribution channel Supplier concentration to firm concentration ratio Employee solidarity (e.g. labor unions) Supplier competition ability to forward vertically integrate and cut out the BUYER
Bargaining Power of Buyers Buyer concentration to firm concentration ratio Degree of dependency upon existing channels of distribution Bargaining leverage, particularly in industries with high fixed costs Buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs Buyer information availability Availability of existing substitute products Buyer price sensitivity Differential advantage (uniqueness) of industry products Key Accounts Chains
Threat of Substitutes Buyer propensity to substitute Relative price performance of substitute Buyer switching costs Perceived level of product differentiation Number of substitute products available in the market Ease of substitution Substandard product Quality depreciation Water vs Cola
Threat of New Competition The existence of barriers to entry (patents, rights, etc.) Economies of product differences Brand equity Switching costs Capital requirements Access to distribution Customer loyalty to established brand Absolute cost Industry profitability; the more profitable the industry the more attractive it will be to new competitors.
Analyzing the Macro Environment Political P Economic E Social S Technological T Legal L Environmental E
Political factors Main concern for business is for stability in political decision making, a dependable planning horizon and a positive climate Alert management to impending legislation Mobilize efforts to represent stakeholder interest to the legislators Develop awareness of the intentions of those public bodies that can make decisions affecting business operations Identify changes out of electoral shifts Implications of Political manifestos and philosophies of the party
Economic factors Business cycle Inflation GDP Economic policies Employment levels Disposable income
Social factors Trends in population Dependency ratio Population structure Occupational structure Regional distribution Marital status and household structure (Case: BMW)
Technological factors Technology is a primary driving force for social change Computer, mobile media and telecommunications are converging Credit transfers rather than cash based society Rise of the knowledge worker Rising proportion of IT and tele communications ownership (Case: Nike)
Ecological factors What are the issues that will directly and indirectly impact the business How will the business mitigate this challenge? Assess stakeholder impact Can the environmental issues be used to ones advantage? What should be our strategic positioning? (Case: Marks & Spencer)
Legal factors Legislation governing business Legislation governing trade practices Laws governing packaging Price ceiling