Master Percentage Increase Reduction Method
This session on February 25, 2025, illustrates the multiplier method for calculating percentage increase and reduction. Learn to determine new prices after changes and avoid overcharging mistakes. Examples include applying discounts and adding VAT. Master this useful skill for accurate pricing decisions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 Calculating Percentage Increase and Reduction The "Multiplier" Method THE STEM CELL
Before we start This slide carries a very important message (c) Glasbergen.com (Reproduced with permission) THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 Calculating Percentage Increase and Reduction The "Multiplier" Method THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 This session will look at how to work out the new cost of an item when a price increase or reduction (as a percentage of the original) is to be applied. It is a useful skill to master. People responsible for "marking up" can make mistakes, if you don't spot these, you could end up being overcharged. It is a useful skill to master. People responsible for "marking up" can make mistakes, if you don't spot these, you could end up being overcharged. THE STEM CELL
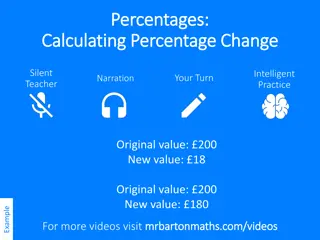
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 The easiest way to approach these problems is to work out a suitable "factor" to multiply the original number by, which would lead us to the new value. Let's work through an example: Your local supermarket is having a sale. All items with the "red sticker" are being offered with a 15% price reduction. You are looking at a new pair of jeans with a price tag of 45. The red tag applies. What would be the cost price of the jeans once the reduction has been applied? Step 1 : Convert the percentage reduction to a decimal number, 15% in this case becomes 0.15 Step 2: The existing price is 100%, 1 as a decimal 1 as a decimal (think about this for a moment, do you see why?) Step 3: As this is a reduction, subtract the reduction decimal from 1 (100% as a decimal) Step 4: 0.85 is your MULTIPLIER. Step 5: Multiply the ORIGINAL PRICE by the MULTIPLIER to get your NEW price: THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 The same method can be used to calculate new prices when an INCREASE is to be applied (more likely to be the case than a reduction!!) The increase is converted to a decimal number and then (this time) ADDED to 1 to make the "multiplier" Let's work through an example: V.A.T. (Value Added Tax) is a purchase tax applied to most goods, the rate varies depending on the item, eg: domestic fuels are taxed at 5% and luxury goods such as electrical appliances 20%. Q1. A laptop computer sells for 359 before VAT is applied. What is the sale price including VAT? Step 1 : Convert the V.A.T. percentage rate to a decimal number, 20% in this case becomes 0.20 Step 2: The existing price is 100%, 1 as a decimal 1 as a decimal (think about this for a moment, do you see why?) Step 3: As this is an increase, we add the increase decimal to 1 (100% as a decimal) Step 4: 1.20 is your MULTIPLIER. THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 Q1. Calculate the new prices of the following items after the increases or deductions have been applied: (a)A red football shirt, priced at 65 is reduced in the sales by 15% (b) A second user (second hand) Ford Mondeo motor car, originally with a sticker price of 14,500 is reduced by 30% (c) A leather motorcycle jacket, priced at 450 is reduced by 22% in an end of season sale. THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 (a)A red football shirt, priced at 65 is reduced in the sales by 15% THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 (b) A second user (second hand) Ford Mondeo motor car, originally with a sticker price of 14,500 is reduced by 30% THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 (c) A leather motorcycle jacket, priced at 450 is reduced by 22% in an end of season sale. THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 Q2. Calculate the new prices of the following items after the increases or deductions have been applied: (a) A litre of petrol, 114.9p increases by 12.5% in the latest budget. (b) A factory worker receives a 6.5% pay increase on his/her hourly rate of 8.45 per hour. From this calculate the new hourly rate. (c) Over a period of 12 months a tree increases in size by 11.5% from it s original height of 7.5m. Calculate the new height in metres. THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 (a) A litre of petrol, 114.9p increases by 12.5% in the latest budget. THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 (b) A factory worker receives a 6.5% pay increase on his/her hourly rate of 8.45 per hour. From this calculate the new hourly rate. THE STEM CELL
Tuesday, February 25, 2025 (c) Over a period of 12 months a tree increases in size by 11.5% from it s original height of 7.5m. Calculate the new height in metres. THE STEM CELL