Mastoiditis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the mastoid air cell system in the skull behind the ear, often caused by untreated ear infections. Learn about its types, signs, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
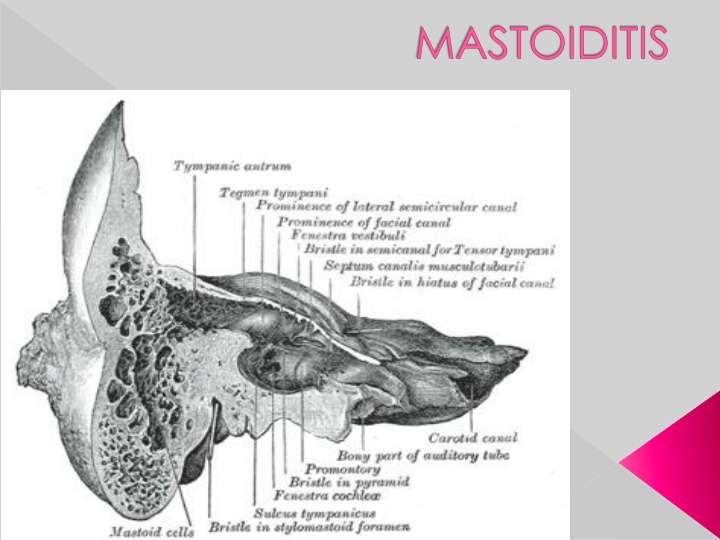
Mastoid process is the portion of the temporal bone of the skull that is behind the ear which contains open, air- containing spaces
it is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the mastoid air cell system inside the mastoid process Mastoiditis is the result of an infection that extends to the air cells of the skull behind the ear
Types Acute mastoiditis - sudden occurrence of inflammation may spread outside the mastoid bone and cause serious problems Chronic mastoiditis in chronic type of mastoiditis there will be ongoing middle ear infection and persistent drainage from the ear.
Causes Mastoidits is usually caused by untreated acute otitis media Cholesteatoma in the middle ear may block drainage of the ear leading to mastoiditis Causative organisms Streptococcus pneumonia, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, heamophilus influenzae and morexalla catarrhalis
Signs and symptoms Pain, tenderness and swelling in the mastoid region Otalgia, redness over the mastoid region Fever , headaches Drainage from the ear occurs in more serious cases Irritability and lethargy
Diagnosis History collection Physical examination MRI CT scan Culture of the drainage Blood tests
Management Antibiotics ceftriaxone IV Myringotomy or tympanostomy to insert a tympanostomy tube into the ear drum to the inner ear for draining. Mastoidectomy a procedure in which a portion of the mastoid bone is removed and the infection drained. A second surgery may do after mastoidectomy to correct the ossicles and the perforated tympanic membrane. (tympanoplasty and ossiculoplasty)
Types of mastoidectomy Simple mastoidectomy surgeon opens the mastoid bone, removes the infected air cells, and drains the middle ear Radical mastoidectomy surgeon remove the eardrum and middle ear structures. Skin graft is placed in middle ear after the procedure Modified radical mastoidectomy this is less severe form of radical mastoidectomy. Not all middle ear bones are removed and the ear drum is rebuilt. Mastoidectomy also done to place choclear implants
Post operative antibiotics and analgesics will be there Follow up date will fix for the removal of stitches and bandage Cover the operative site while bathing (pertroleum jelly covered cotton ball) Avoid streneous activity Avoid air travel Avoid putting pressure on ear
Complications If left untreated it can cause hearing loss, blood clot, meningitis and brain abscess Complications of surgery Facial nerve paralysis Sensorineural hearing loss Vertigo Change in taste (metallic taste) Tinnnitus