Maternal-Fetal Medicine Insights: Uterine Stimulants, Amniotic Fluid, and Fetal Physiology
Key factors affecting myometrial contractility, amniotic fluid dynamics, and fetal cardiovascular physiology in maternal-fetal medicine. Learn about endogenous uterine stimulants, contributors to amniotic fluid volume, and critical fetal organ perfusion. Understand the implications of umbilical cord blood gas analysis, hypoxic events, and diagnostic radiation procedures in obstetrics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1 Which of the following factors is endogenous uterine stimulant affecting myometrial contractility during labor? A. Corticotropin releasing hormone B. Parathyroid hormone related protein C. Placental like growth factor D. Endothelin E. Prostaglandin inhibitors Answer: D (Creasy & Resnik s Maternal-Fetal Medicine 6thEd, Chapter 5 Biology of Parturition, p 80)
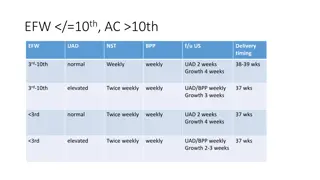
2 Which of the following sources is NOT the contributor to amniotic fluid volume in the third trimester of pregnancy? A. Fetal urine B. Fetal lung fluid C. Fetal skin D. Transudation across the umbilical cord E. Transudation across the placenta Answer: C (Creasy & Resnik s Maternal-Fetal Medicine 6thEd, Chapter 3 Amniotic fluid Dynamics, p 48-49)
3 Which of the following fetal organs is perfused by the highest percentage of total cardiac output? A. Brain B. Heart C. Lungs D. Upper limbs E. Lower limbs Answer: E (Creasy & Resnik s Maternal-Fetal Medicine 6thEd, Chapter 12 Fetal Cardiovascular Physiology, p 161-162)
4 According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, umbilical cord blood gas and pH analyses should be obtained in the following circumstances for immediate or long term neurological outcome prediction, EXCEPT? A. B. C. D. E. Abnormal fetal heart rate tracing Intrapartum fever Multifetal gestation Forceps delivery and vacuum extraction Low 5-minute Apgar score Answer: D (Williams Obstetrics 23rdEd, Chapter 28 The newborn infant, p 598)
5 Which of the following criteria is an essential criterion to define an acute intrapartum hypoxic event sufficient to cause cerebral palsy? A. B. C. D. E. Umbilical cord blood pH < 7.2 Umbilical cord blood base deficit of > 12 mmol/L Cerebral palsy of spastic diplegia type Cerebral palsy of ataxic type Early onset of severe neonatal encephalopathy in infants born at < 34 weeks Answer: B (Williams Obstetrics 23rdEd, Chapter 29 Diseases and injuries of the fetus and newborn, p 612)
6 Which of the following diagnostic radiation procedure results in the highest dose to fetus? A. Upper gastrointestinal series B. CT Pelvimetry, low-exposure technique C. Intravenous pyelogram, 3 views D. Barium enema E. Plain film abdomen, AP view Answer: C (Williams Obstetrics 23rdEd, Chapter 41 General considerations and maternal evaluation, p 916-919)
7 Which of the following fetal cardiac malformations is the least likely diagnosis when normal four chamber view is found by ultrasound examination at 22 weeks of gestation? A. B. C. D. E. Truncus arteriosus Tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia Tetralogy of Fallot with absent pulmonary valve Double outlet of right ventricle D-transposition of the great arteries Answer: C (Creasy & Resnik s Maternal-Fetal Medicine 6thEd, Chapter 19 Fetal Cardiac Malformations and Arrhythmias, p 332-334)
8 According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, which condition does NOT indicate for antepartum electronic fetal monitoring? A. B. C. D. E. History of previous unexplained third trimester fetal demise Moderate isoimmunization Polyhydramnios Dichorion diamnion twin pregnancy Poorly controlled hyperthyroidism Answer: D (ACOG practice bulletin Number 9, October 1999, reaffirmed 2012)
9 According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, which statement is TRUE about the use of chromosomal microarray analysis in prenatal diagnosis? A. B. It is restricted to women aged 35 years and older. It is not recommended in patients with a fetus with one major structural abnormality undergoing invasive prenatal diagnosis. It is not recommended in patients with a structurally normal fetus undergoing invasive prenatal diagnosis. It is not recommended in first trimester pregnancy loss evaluation. It is not recommended in cases of intrauterine fetal demise when cytogenetic analysis is desired. C. D. E. Answer: D (ACOG committee opinion Number 581, December 2013)
10 According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, which statement is TRUE about prediction of preeclampsia? A. B. sFlt-1 is rising 4 5 weeks before onset of preeclampsia PlGF and sFlt-1 biomarker screening is recommended for preeclampsia prediction in high risk cases. Screening to predict preeclampsia by obtaining a history only is not recommended. Uterine artery Doppler screening is better at predicting late-onset preeclampsia than early-onset preeclampsia. sFlt-1/PlGF ratio is a test that reliably predicts preeclampsia. C. D. E. Answer: A (ACOG, November 2013)
11 A 24-year-old nulliparous 20 weeks of gestation came with history of fetal sinus bradycardia. An ultrasound exam showed normal fetus without hydrops. Fetal ventricular heart rate was regularly 60 70 beats/min with 2:1 conduction. What is the most appropriate next step management? A. B. C. D. E. Close observation A-A interval measurement A-V time measurement Maternal anti-Ro and anti-La antibodies testing Maternal treatment with dexamethasone Answer: B (Creasy & Resnik s Maternal-Fetal Medicine 6thEd, Chapter 19 Fetal Cardiac Malformations and Arrhythmias, p 338)