Mechanics of Materials: Combined Loading Analysis & Examples
Explore the concept of combined loading in mechanics of materials, including axial, torsional, bending, and shear stresses. Learn how to analyze and solve problems involving compound shafts, rotor shafts in helicopters, and more using superposition principles. Dive into examples and solutions for a comprehensive understanding.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mechanics of Materials Engr 350 Lecture 35 Combined Loading AKA: SuperPosition is Still Awesome
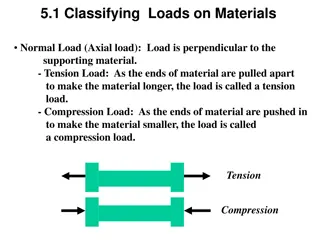
Stress toolbox We ve investigated the following ? =? Axial ? ?? ? Torsional ? = ?? ? Bending ? = ?? ?? Shear ? = Many components are subjected to multiple types of loading we need to determine what the resulting loading is at the critical points May use Superposition as long as the combination of stresses are still in the elastic (linear) region 2
Combined axial and torsional loads Consider the stress on the rotor shaft of a helicopter Both axial and torsional loading Where is axial stress highest? Where is torsional stress highest? 3
= 8 kN-m = 12 kN-m Example Problem 1 = 100 kN A compound shaft consists of two pipe segments. Segment (1) has an outside diameter of 220 mm and a wall thickness of 10 mm. - Determine the magnitude of the stresses on element at H. 4
Example Problem 3 Consider the clamp 7