Mechanism of Elementary Reactions for Rate Equation
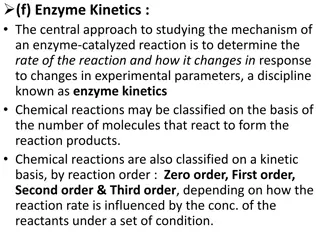
In this exercise, a mechanism of elementary reactions is devised to align with the given rate equation involving a chain reaction with a chlorine atom intermediate. The process involves building the mechanism step by step, focusing on initiation, propagation, and termination steps. By balancing the mechanism and checking against the overall reaction and rate equation, a comprehensive understanding is achieved. Through this exercise, the concept of radical formation, radical propagation, and radical termination in chemical reactions is explored.
Uploaded on Apr 29, 2025 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Calculation Session 13 Exercise 4 Created by: Sakul Ratanalert ( 11) Revised by: Justin Rosch (grad), Carl Schultz ( 15), Michael Statt ( 16), Charles Wan ( 17), Michaela Jones ( 18), Praveen Bagavandoss ( 19), Sarah Paquin ( 21), Kaleigh Soucy ( 23), Ashlyn Dumaw ( 25), Lara Capellino ( 26)
Goal: Devise a mechanism of elementary reactions consistent with the rate equation Info: An overall reaction and rate equation Chain reaction, Cl atom intermediate Where to start: Use the hint! Start with the chlorine atom
Building the Mechanism Reactant Chlorine intermediate Now, we need to use the chlorine intermediate SO2Cl SO2Cl SO2Cl2 SO2Cl2 + Cl + Cl We want to: Form the products Produce a radical (required for a propagation cycle) Use reactants ` + Cl + Cl SO2Cl SO2Cl SO2Cl2 SO2 + Cl2 SO2 + Cl2 SO2Cl + Cl2 + Cl
Building the Mechanism initiation propagation SO2Cl SO2 + Cl We still need to: Use SO2Cl Produce SO2 Produce Cl in a propagation step Have a termination step
Building the Mechanism initiation propagation propagation We still need to: Have a termination step Consume radicals SO2Cl + Cl SO2Cl + Cl SO2Cl + SO2Cl Cl + Cl M + Cl + Cl Cl2 + M SO2Cl2 SO2 + Cl2 ClSO2SO2Cl Cl2 simple! complicated - unlikely termolecular - unlikely
Final Mechanism initiation/termination propagation propagation Good practice: check the overall reaction
Balancing Our Mechanism initiation/termination propagation propagation Balance only the propagating steps!
Balancing Our Mechanism initiation/termination propagation propagation
Final Mechanism initiation/termination propagation propagation Good practice: check the overall rate equation
Checking the Rate Equation Need an expression for [ SO2Cl] Rate of initiation = rate of termination Need an expression for [Cl ] Rate of propagation, 2 = rate of propagation, 3 Plug the expression for [Cl ] into [ SO2Cl]
Checking the Rate Equation Solve for [ SO2Cl] Substitute into original rate law equation
Final Mechanism k2 k3 Visualize with a propagation cycle!
Key Takeaways Keep it simple (intuitive elementary steps) Important assumptions: Steady state Rate of initiation = Rate of termination Rate of propagation for both radicals equal Check your expression when possible! Use propagation cycles to visualize the process
Team Competition B+C mixtures A+C mixtures