Mechanisms and Simulations of Nitrates in Gas and Aerosol Phases
This content discusses the mechanisms and simulations related to nitrates in gas and aerosol phases. It covers the yields for second-generation calculations, decomposition products, higher generation yields, and species types in aerosol. The figures and images included provide detailed insights into the processes and products involved in the chemistry of nitrates.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
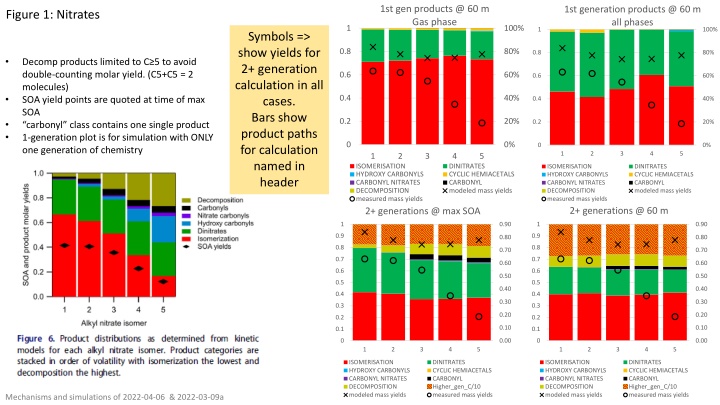
1st gen products @ 60 m Gas phase 1st generation products @ 60 m all phases Figure 1: Nitrates 1 100% 1 100% Symbols => show yields for 2+ generation calculation in all cases. Bars show product paths for calculation named in header 0.8 80% 0.8 80% Decomp products limited to C 5 to avoid double-counting molar yield. (C5+C5 = 2 molecules) SOA yield points are quoted at time of max SOA carbonyl class contains one single product 1-generation plot is for simulation with ONLY one generation of chemistry 0.6 60% 0.6 60% 0.4 40% 0.4 40% 0.2 20% 0.2 20% 0 0% 0 0% 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION measured mass yields 2+ generations @ max SOA DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL modeled mass yields ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION measured mass yields DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL modeled mass yields 2+ generations @ 60 m 1 0.90 1 0.90 0.9 0.9 0.80 0.80 0.8 0.8 0.70 0.70 0.7 0.7 0.60 0.60 0.6 0.6 0.50 0.50 0.5 0.5 0.40 0.40 0.4 0.4 0.30 0.30 0.3 0.3 0.20 0.20 0.2 0.2 0.10 0.10 0.1 0.1 0 0.00 0 0.00 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION modeled mass yields DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL Higher_gen_C/10 measured mass yields ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION modeled mass yields DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL Higher_gen_C/10 measured mass yields Mechanisms and simulations of 2022-04-06 & 2022-03-09a
1st gen products @ 60 m Gas phase 1st generation products @ 60 m all phases Figure 1: Nitrates 1 100% 1 100% Decomp products limited to C 5 to avoid double- counting molar yield. (C5+C5 = 2 molecules) SOA yield points are quoted at time of max SOA carbonyl class contains one single product 1-generation plot is for simulation with ONLY one generation of chemistry 0.8 80% 0.8 80% 0.6 60% 0.6 60% 0.4 40% 0.4 40% Symbols and bars refer to calculation named in header in every case 0.2 20% 0.2 20% 0 0% 0 0% 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION measured mass yields 2+ generations @ max SOA DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL modeled mass yields ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION measured mass yields DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL modeled mass yields 2+ generations @ 60 m 1 100% 1 100% 0.9 0.9 0.8 80% 0.8 80% 0.7 0.7 0.6 60% 0.6 60% 0.5 0.5 0.4 40% 0.4 40% 0.3 0.3 0.2 20% 0.2 20% 0.1 0.1 0 0% 0 0% 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION modeled mass yields DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL Higher_gen_C/10 measured mass yields ISOMERISATION HYDROXY CARBONYLS CARBONYL NITRATES DECOMPOSITION modeled mass yields DINITRATES CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL Higher_gen_C/10 measured mass yields Mechanisms and simulations of 2022-04-06 & 2022-03-09a
Figure 2 decan-3-nitrate: top 20 species types in Aerosol @ max aer C6H12O2 THE C10H20N2O8 NNHH C10H19N3O10 NNNH C10H18O3 TCHE Colors show species type excluding original nitrate group: N, Blue, nitrate ( N in GECKO convention); H, Yellow, hydroxy ( O ); C, Orange, carbonyl ( D or K ); U, Green, unsaturated ( U ); TE, Black outline, cyclic ether ( TE ) C10H17N1O4 TNUE C10H17N1O5 TNUHE C10H18O4 CCHE C7H14O2 THE Molecular formula C10H17N3O10 TNNNE C10H18N2O8 NNCH C10H19N1O6 TNHHE C10H19N3O9 NNN C10H20O3 THHE C10H18N2O8 TNNHE C10H20O2 THE C10H19N1O5 NCH C10H20N2O7 NNH C10H17N1O6 NCCE C10H20N2O6 NN C10H19N1O5 TNHE 0.0E+00 1.0E+12 2.0E+12 3.0E+12 conc in aerosol, molec/cc_air Mechanisms and simulations of 2022-03-09 a
Figure 3: Products @ time of peak aerosol decane-nitrate products @ SOA maximum concentration, molec.cm-3 air equivalent 1.4E+13 total wall particle gas 1.2E+13 1E+13 8E+12 6E+12 4E+12 2E+12 0 1 3 5 1 3 5 1 3 5 1 3 5 isomer: initial position of ketone group ISOMERISATION DINITRATES HYDROXY CARBONYLS CYCLIC HEMIACETALS CARBONYL NITRATES CARBONYL DECOMPOSITION 3RD-GEN-C/10 Mechanisms and simulations of 2022-03-09 a






















