Mechanisms: Coleman Boat Model and Behavioral Examples
Explore the different types of mechanisms such as Transformational, Situational, and Action-formation within the context of Coleman boat model. Learn about situational mechanisms like the definition of the situation and opportunity structures, action-formation mechanisms such as cognitive dissonance and social validation, and transformational mechanisms like markets and self-fulfilling prophecies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
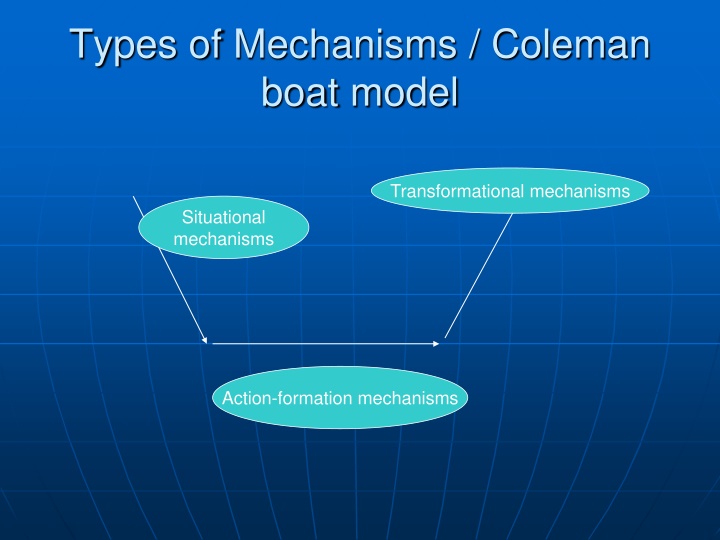
Types of Mechanisms / Coleman boat model Transformational mechanisms Situational mechanisms Action-formation mechanisms
EXAMPLES OF SITUATIONAL MECHANISMS: The definition-of-the-situation ( if men define situations as real they are real in their consequences ; behavior settings and their temptations , provocations, and level of deterrence ( Wikstrom & Sampson, 2003)
EXAMPLES OF SITUATIONAL MECHANISMS: Opportunity structures ( such as a vacancy chain or the openness of communities for burglars) a community s level of its three R s: resources, rules and routines (Wikstrom, 1998)
EXAMPLES OF ACTION-FORMATION MECHANISMS: Cognitive dissonance (i.e. the force to reduce D); innovation diffusion processes (i.e. the force to innovate or not), prisoner games (the force to trust, to accept, to accommodate or to kill ) social capital (the force to bond or not) Social validation of judgments /obedience to authority Relative deprivation (if I move up but s.i s move up quicker, then ) Discounting ( the acceptance rate of losses) Bounded will power ( to know that acting X is dangerous but nevertheless do it) different types of learning behaviour (like vicarious learning) ; propensity ( is primarily made up of specific cognitive and emotional Characteristics that jointly determine morality and self-control ) Sunk costs
EXAMPLES OF TRANSFORMATIONAL MECHANISMS: Markets ( to transfer individual options to larger entities) veto power ( what has been done bottom up , has no effect when there is someone with veto power) Self-fulfilling prophecy (by doing x, the opposite will be realized/ effects pervers ) collective good processes ( when large groups and collective good production is involved, than free rider behaviour will take place, hence no transformation