Meiosis Process and Terminology
Explore the intricacies of meiosis, the type of cell division that produces germ cells like eggs and sperm. Discover the stages of meiosis, genetic variation, karyotype, and more. Dive into the world of genetics and reproductive biology through detailed explanations and visuals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Q2 WK3 D2 MEIOSIS
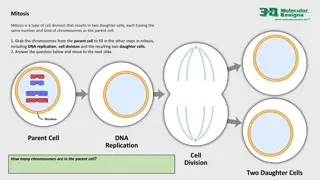
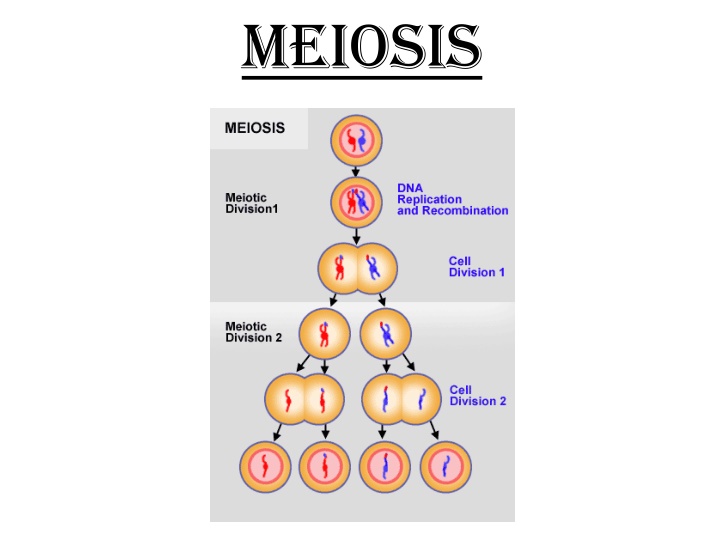
Meiosis Meiosis Meiosis is thetype of cell division by which germ cells (eggs and sperm) are produced. One parent cell produces four four daughter cells. Daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes found in the parent cell
Meiosis During meiosis, DNA replicates once, but the nucleus divides twice. There are 2 parts to Meiosis: 1. Meiosis 1 2. Meiosis 2 The 4 new daughter cells have variation of the parent DNA; this is genetic variation
Meiosis Terminology Karyotype: Arranging of chromosomes from largest to smallest; pairing up the homologous chromosomes Autosomes: All non-sex chromosomes; (#1-22 for humans) Sex Chromosomes: Chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism (#23 for humans) Set (n): # of different chromosomes. REMEMBER: Haploid = 1set, Diploid= 2 sets
Karyotype of a human Is this person male or female? http://www.biologyjunction.com/karyotype_female.jpg How many sex chromosomes are present? How many autosome chromosomes are present? How many homologous pairs of chromosomes are present?
Background on Meiosis Meiosis involves 2 divisions of the nucleus Meiosis 1 & Meiosis 2 Meiosis STARTS with HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Homologous Chromosomes: They are similar in shape, size & genetic content
Meiosis 1: 1st Division of Meiosis Prophase I: Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks, homologous chromosomes pair at ends. ***Cross-Over: Part of chromatid on 1 homologous chromosome exchanges with the other chromosome***
Meiosis 1: 1st Division of Meiosis Metaphase I: Homologous chromosomes move to center of the cell by the spindle fibers. Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles, BUT sister chromatids stay together. A set of chromosomes moves to each pole Telophase I: The spindle fibers disappear, cells begin to cleave; still, two sets of chromosomes are at opposite poles
Meiosis 1 http://www.t21world.egytefl.org/image%20of%20gallery/1%20(15).gif
End of Meiosis I http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab3/images/stages2.gif Once Meiosis I is complete, cytokinesis occurs and the cell splits into 2 haploid cells. These 2 cells enter Meiosis II
Meiosis I: STOP & THINK 1. What is the purpose of Meiosis? http://images.sodahead.com/polls/001904507/133453699_thinking20web20pic_xlarge.jpeg 2. Describe genetic variation 3. Explain purpose of karyotyping 4. Explain cross-over 5. What major event occurs in Anaphase I ? 6. Are the daughter cells haploid or diploid? Explain
Meiosis I: Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1_- mQS_FZ0
Meiosis II Meiosis II Prophase II: A new spindle forms around the chromosomes (no longer HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES) Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at center & spindle fibers attach to centromere Anaphase II: Centromeres split, chromatids move to opposite poles of cell Telophase II: Nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes & spindles retracts, cell begins cytokinesis
Result of Meiosis II Result of Meiosis II 4 HAPLOID cells form as a result of Meiosis II Haploid = cell containing 1 set of chromosomes
Prophase II http://everyschool.org/u/logan/cellreproductionx/rogersa/research/meiosis.html
Metaphase II http://everyschool.org/u/logan/cellreproductionx/rogersa/research/meiosis.html
Telophase II http://everyschool.org/u/logan/cellreproductionx/rogersa/research/meiosis.html
Meiosis I & II Venn Diagram Meiosis I & II Venn Diagram Meiosis I Meiosis I Meiosis II Meiosis II
Meiosis Booklet 1. Everyone needs 3 sheets of blank paper 2. Fold each one hotdog style 3. Cut straight up the fold (You should have 6 long sheets, only use 5) 4. Label each square with the phases of meiosis the same as the mitosis booklet
Meiosis Review Questions 1. What type of cells are used in Meiosis? Give examples of these cells. 4.Meiosis is divided into two parts, why? 5. Define Haploid 2. Meiosis is used in sexual reproduction. Explain the process of cross-over 6. Compare and Contrast Meiosis to Mitosis. 3. Draw homologous chromosomes going through cross-over.
Mitosis & Meiosis Comparison Worksheet http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/baby/divi_flash.html http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/curr/science/sciber00/7th/gen etics/sciber/animatin.htm
Nov. 5th, 2013 Q2 WK4 D2 Meiosis & Genetic Variation