Memorandum of Association in Company Law
The memorandum of association in company law defines the structure, powers, and constraints of a company. It serves as the foundation on which the company operates, setting out its permissible activities, purpose, and contractual boundaries. Learn about the nature, purpose, forms, and requirements of the memorandum of association in this comprehensive guide.
Uploaded on | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
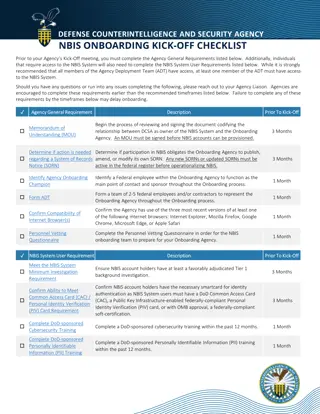
Chapter 5 Memorandum of Association 1. Nature and definition of memorandum of association The memorandum of Association is a document which sets out the constitution of company and is the foundation on which the structure of the company is based. The memorandum of association does not only define the structure and power of the company but also confine the power of the company through the principle of Ultra virus.
2. Purpose of Memorandum of Association a) It enables shareholders, creditors and those who deal with the company to know what exactly is the permitted range of activities of the company. b) It enables these parties to know the purpose for which their money is going to be used by the company and the nature and extent of risk they are undertaking in making investment. c) It enables the parties dealing with the company to know with certainty as whether the contractual relation to which they intend to enter with the company is within the objects
of the company. 3. Form Memorandum of Association In company law, usually there are four forms of memorandum of association and they are: a) form of Memorandum of a company limited by shares; b) Memorandum of a company limited by guarantee and not having a share capital; c) Memorandum of company limited by guarantee and having share capital; and d) Memorandum of an unlimited company.
The Memorandum of Association of a company shall be: (a) printed, (b) divided into paragraphs numbered consecutively, and (c) signed by prescribed number of subscribers (7 or more in the case of public company, two or more in the case of private company respectively). Each subscriber must sign for his/her name, address, description and occupation in the presence of at least one witness who shall attest the signature and shall likewise add his address, description and occupation, if any.
Subscribing means to append one s signature or mark a document as approval of its content. Contents of Memorandum of Association: 1. Name Promoters of the company have to make an application to the registrar of Companies for the availability of name . To be use the word of limited as the last word of its name if it s a limited company. The name that has been registered may be changed by special resolution of the company without having any effect on its rights and obligations.
2. Registered Office Registered Office of a company is considered as the residence of the company for the purpose of delivering or addressing any communication, service of any notice or process of court of law and for determining question of jurisdiction of courts in any action against the company. It is also the place for keeping statutory books of the company. Registered office gives the company physical residence.
3: Objects of the company This is the most important clause in the memorandum because it not only shows the object or objects for which the company is formed but also determines the extent of the powers which the company can exercise in order to achieve the object or objects. The following should be observed in choosing object of the company: it should not be illegal it should not be included anything in contravention of the company law it should not be included anything against Public policy
the objects clause may the following sub clause: i) Main Objects : This sub-clause has to state the main objects to be pursued by the company on its incorporation and objects incidental or ancillary to the attainment of main objects. ii) Other objects: This sub-clause shall state other objects which are not included in the above clause. A company, which has a main object together with a number of subsidiary objects cannot continue to pursue the subsidiary objects after the main object has come to an end.
In order to avoid the effect of the ultra vires principle; experts come up with three types of object clauses which are: inflated object clause Independent object clause Subjective object clause 4. Liability clause The promoters must indicate whether the company is limited or unlimited. If the company is limited, is it limited by share or by guarantee? If the company is unlimited; the liability clause is omitted.
5.The capital Memorandum shall also state the amount of share capital with which the company is to be registered and division there of into shares of a fixed amount. The nominal capital is divided into classes of shares and their values are mentioned in the clause. In case of companies limited by guarantee, the amount promised by each member to be contributed by them in case of the winding up of the company has to be mentioned.
6. Subscription or Association Clause In this clause, the subscribers declare that they desire to be formed into a company and agree to take shares stated against their names. The signature of each subscriber must be attested by at least one witness who cannot be any of the subscribers. Each subscriber and his witness shall add his address, description and occupation, if any.
7. Alteration of Memorandum of Association Alteration of Memorandum of association involves compliance with detailed formalities and prescribed procedure. Alternations to the extent necessary for simple and fair working of the company would be permitted. Alterations should not be prejudicial to the members or creditors of the company and should not have the effect of increasing the liability of the members and the creditors.
Contents of the Memorandum of association can be altered as under : a. name of the company and its registered office b. object of the company with the following purposes: i. to enable the company to carry on its business more economically or more effectively; ii. to enable the company to attain its main purpose by new or improved means; iii. to enlarge or change the local area of the company s operation;
iv. to carry on some business which under existing circumstances may conveniently or advantageously be combined with the business of the company; v) to restrict or abandon any of the objects specified in the memorandum vi) to sell or dispose of the whole, or any part of the undertaking of the company; vii) to amalgamate with any other company or body of persons.
Any alteration in previous mentioned documents should be delivered a copy of it to the registrar. Doctrine of ultra virus A company cannot go beyond its power given in the memorandum. A company shall not engage in any activity which is authorized expressly or impliedly in the memorandum, and if does that; there shall not any act of ratifying it and it shall be void. Acts of directors of the company which are ultra vires may ratified by the share holders through special resolution.
Effect of ultra vires transaction a. Null and void b. Injunction c. Personal liability of directors for ultra vires payments d. Liability for breach of warranty of authority e. Company may retain property acquired for the payment of its money under the principle of Ultra Virus.