Menstruation: The Menstrual Cycle Explained
Explore the detailed process of the menstrual cycle, from the shedding of the uterine lining to the release and potential fertilization of an egg. Learn about the hormonal changes that drive this cycle and the possibility of pregnancy. Find out how to track and understand your body's natural rhythm.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
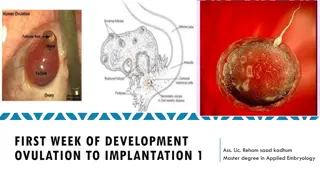
Day 1: Menstruation begins (this is often called having your period ).
Lining of the uterus (endometrium) is no longer needed so it sheds through the vagina releasing blood, mucus, and tissue.
Menstruation usually lasts anywhere from 3-10 days.
Hormones send a signal to your body to begin thickening the lining in the uterus (endometrium).
Lining of the uterus (endometrium) continues to build up and prepares to nourish a fertilized egg.
Hormones continue to rise, triggering an egg to release from one of your ovaries.
Ovaries release a mature egg which travels down the fallopian tube for approximately 24 hours.
The egg can only be fertilized when traveling through the fallopian tube.
The egg reaches the uterus around day 14 of the cycle (but can be different for everyone).
If the egg is fertilized while in the fallopian tube, the egg will attach to the uterine wall and pregnancy can occur. If not, the egg will begin to dissolve in the uterus.
If pregnant, the body will increase hormone production over the next 10 days and menstruation will not occur.
If not pregnant, hormone levels decrease over the next 10 days and will trigger menstruation (a period).