Microflora, Extremophiles, Nutrition Modes, Parasitism, and Symbiosis in Ecology
Explore the diverse habitats of microflora in soil, rivers, oceans, and lakes. Learn about extremophiles thriving under extreme pH and temperature conditions. Delve into various modes of nutrition, including saprophytism and parasitism. Discover the symbiotic relationships of microorganisms with plants. Uncover the essential resources for organism growth in ecosystems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
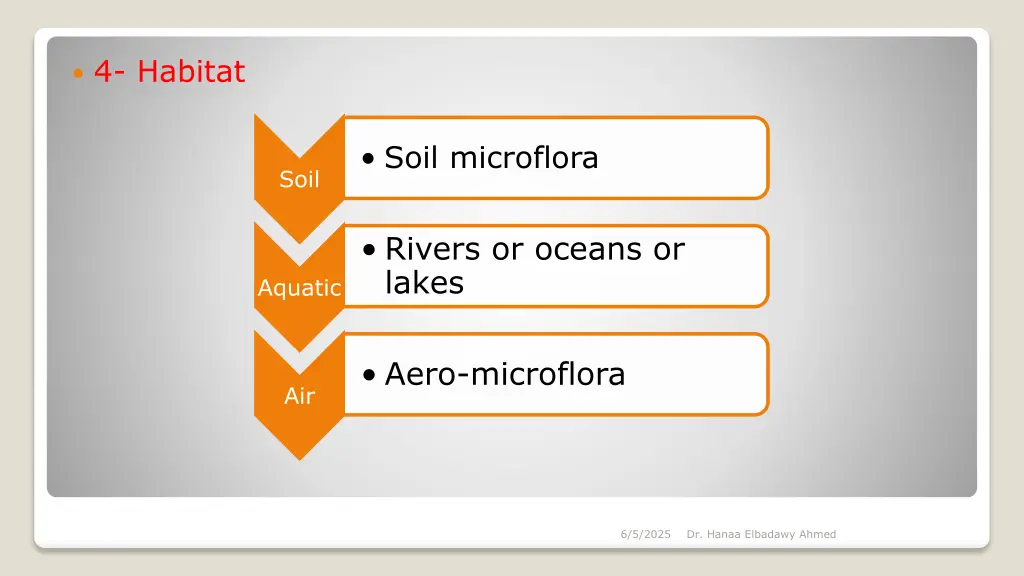
4- Habitat Soil microflora Soil Rivers or oceans or lakes Aquatic Aero-microflora Air 6/5/2025 Dr. Hanaa Elbadawy Ahmed
5- Extremophiles such as: - live at high or low pH. (5- 9 are the common range) Acidophiles Alkaliphiles Hyperthermophile Psychrophiles. 6/5/2025 Dr. Hanaa Elbadawy Ahmed
6- Mode of nutrition: Saprophytism : With the help of ? (pp.7) Examples ? Sometimes shift to parasitism. 6/5/2025 Dr. Hanaa Elbadawy Ahmed
Parasitism: - Obligate, very virulent cannot live without the host. e.g. Puccinia causes rust disease for cereal - Facultative saprophytes, e.g 1- Phytophthora .. Late blight of potato, can be cultured in lab on oat agar medium. 2- Taphrina .. Cause leaf curl of peach 6/5/2025 Dr. Hanaa Elbadawy Ahmed
Symbiosis (Beneficial associations): 1- Cyanobacterial symbiosis. 2- Actinomycetes non-legume plants. 3- bacterial symbiosis; i-Associative symbionts ii- Legume- Rhizobium symbionts(forming nodules). iii- PGPR (plant growth promoting rhizobacteria) 4- Fungal symbiosis. i- Ectomycorrhizae. ii- Endomycorrhizae. iii- Ectendomycorrhizae. 6/5/2025 Dr. Hanaa Elbadawy Ahmed
Resources Any substance or factor consumed by an organism that lead to its growth included a) essential, b) substitutable resources . a) Essential or Cardinal elements C, N, S Essential acceptors O2, NO3, Fe++ ,SO4-- Electron pH, Temp., Salinity, other limit organisms Abiotic factors P, K, Mg, Inorganic element s Vitamins Organic compou nds 6/5/2025 Dr. Hanaa Elbadawy Ahmed





