Middle Ear Infections: Overview, Classification, and Management
Explore the world of middle ear infections (otitis media) with this comprehensive guide covering definitions, anatomy, classification, epidemiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, and more. Learn about the clinical features, diagnostic approaches, and management of OM, along with common complications. Ideal for students, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in microbiology and ear health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
M Microbiology icrobiology of M Middle iddle E Ear of ar I Infections nfections DR. ALI DR. ALI SOMILY SOMILY, MD , MD
Objectives Upon completion of the lecture , students should be able to: Define middle ear infection Know the classification of otitis media (OM). Know the epidemiology of OM Know the pathogenesis & risk factors of OM. List the clinical features of OM. Know the diagnostic approaches of OM. Know the management of OM. Recall common complications of OM.
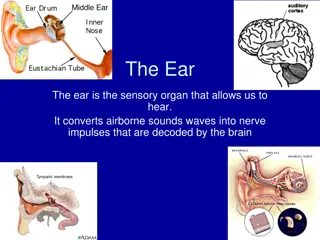
Definitions Definitions Middle ear is the area between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear including the Eustachian tube. Otitis media (OM) is inflammation of the middle ear.
OM OM- -Classification Classification Acute OM Secretory ( Serous) OM http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:1tH2Q7X7lqkCwM:http://www.middleearimplants.com/images/fully-implantable-middle-ear-device.jpg Chronic OM
http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:F1j8DXYrYIv89M:http://www.alleganyhealthdept.com/images/infant.pnghttp://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:F1j8DXYrYIv89M:http://www.alleganyhealthdept.com/images/infant.png OM OM- - Epidemiology Epidemiology Most common in infants 6 to 18 months of age (2/3 of cases). Improves with age, why ? The Eustachian Tube which vents the middle ear to the nasopharynx , is horizontal in infants, difficult to drain naturally, its surface is cartilage ,and lymphatic tissue lining is an extension of adenoidal tissue from back of the nose. Accompanied with viral URTI http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:R9V79ruGIs2kaM:http://content.onestepahead.com/assets/images/product/detail/13735_1.jpg
OM OM- -Pathogenesis and Risk Factors Pathogenesis and Risk Factors URTI or allergic condition cause edema or inflammation of the tube. Functions of the tube (ventilation, protection and clearance) disturbed. Oxygen lost leading to negative pressure Pathogens enter from nasopharynx into middle ear. Colonization and infection result. http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:by3MmKmS-3rwXM:http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75719/Pictures%2520Library/Respiratory%2520system/Upper%2520respiratory%2520tract.jpg
OM OM- - Other risk factors Other risk factors Anatomic abnormalities Medical conditions such as Cleft palate ,obstruction due to adenoid or NG tube or malignancy, immune dysfunction. Exposure to pathogens from day care. Exposure to smoking. http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:J3ptxBEM_0ul-M:http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/figures/1471-2350-5-15-1.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:xqzWfJzPWrDXrM:http://buckheadent.net/images/tons.gif
Images of acute OM Images of acute OM http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:f0Vfl7IkhnkVjM:http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/39/Otitis_media_incipient.jpg http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:qDwZNRe8K2SM0M:http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/medicine/pulmonar/pdself/Serous_ottitis_media.jpg http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ewRNPlXlpEjGlM:http://de.academic.ru/pictures/dewiki/79/Otitis_media_schollig.jpg
Images of chronic OM http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:Xmx1Gilw3kPdRM:http://www.evmsent.org/images/tmperf.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:1SDGBm5dQug-kM:http://www.uthsc.edu/otolaryngology/images/567.jpg
Images of serous OM Images of serous OM http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:1QsfEh0rhFpSaM:http://www.rcsullivan.com/www/toml0911.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:VXNqbOkLsY1mmM:http://www.fpnotebook.com/_media/EntSerousOtitisMedia.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:-obOj53sdnbekM:http://www.texasent.com/userfiles/image//Otitis%2520Media%2520Fig3.JPG
Microbiology of OM Microbiology of OM http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:avYNveKQwqRGfM:http://www.msevans.com/cnsinfections/h-influenzae.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:Na9KOCmMV9oAwM:http://www.gslabs.com/images/saureus2.jpg http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:MGJUENYImbkqwM:http://textbookofbacteriology.net/themicrobialworld/S.pneumoniae1.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:MkzqdnjQrCYNzM:http://www.mc.maricopa.edu/~johnson/labtools/Dbiochem/opto4b.jpg http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:I37L4EcCa2rF5M:http://farm3.static.flickr.com/2240/2402321868_539a568ec7_o.jpg http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:mlz6bFjW6h_T-M:http://www.vetbact.org/vetbact/include/getvetbaktimage.php%3Fimgid%3D238%26imgtable%3Dvetbact_images%26images%3D0
Microbiology of OM Microbiology of OM- -continue continue Go to fullsize image Go to fullsize image Go to fullsize image Go to fullsize image Go to fullsize image Go to fullsize image Go to fullsize image
OM OM- -Microbiology Microbiology- -Bacterial Causes Bacterial Causes Acute OM Acute OM < 3months of age S.pneumoniae,(40%) group B Streptococcus, H.influenzae (non typable), Gram negative bacteria and P. aeruginosa > 3 months of age S.pneumoniae, H. influenzae, others eg, S. pyogenes, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. aureus
OM OM- -Microbiology Microbiology- -cont. cont. Chronic OM Chronic OM Mixed flora in 40% of cases P.aeruginosa, H.influenzae, S.aureus, Proteus species, K.pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobic bacteria. Serous OM Serous OM Same as chronic OM, but Most of the effusions are sterile Few acute inflammatory cells
OM OM- -Viral causes Viral causes http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:gIH_nUuEjo67FM:http://template.bio.warwick.ac.uk/staff/easton/IMAGES/Diagrams/3dvirus.jpg RSV -74% of viral isolates Rhinovirus Parainfluenza virus Influenza virus
Clinical presentation Clinical presentation Acute OM Mostly Bacterial ,often a complication of viral URTI First 1 First 1- -2 days Fever (39 C), irritability, earache (otalgia), muffled nose. 2 days: Bulging tympanic membrane ,poor mobility and obstruction by fluid or inflammatory cells on otoscopic examination.
3 3- -8 days: 8 days: Pus and ear exudate discharge spontaneously (otorrhea) and pain and fever begin to decrease. 2 2- -4 weeks : 4 weeks : Healing phase, discharge dries up and hearing becomes normal.
Serious OM Serious OM Collection of fluid within the middle ear as a result of negative pressure produced by altered eustachian tube function. Represent a form of chronic OM or allergy-related inflammation Tends to be chronic , with non purulent secretions. Cause hearing deficit.
Chronic OM Chronic OM Usually result from unresolved acute infection due to in adequate treatment or host factors that perpetuate the inflammatory process. Result in destruction of middle ear structures and significant risk of permanent hearing loss.
Diagnostic approaches of OM Diagnostic approaches of OM Clinical examination Tympanometry ( detect presence of fluid) Gram stain and culture of aspirated fluid to determine the etiologic agents. http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:qDwZNRe8K2SM0M:http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/medicine/pulmonar/pdself/Serous_ottitis_media.jpg http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:9V291FPaYcZ7lM:http://www.tchain.com/otoneurology/testing/images/audio5.gif
Management of OM Management of OM Acute OM requires antimicrobial therapy & careful follow up. Antimicrobial usually empirical depending on the most likely bacterial pathogens, usually to cove S.pneumonia and H.influenzae. Drainage of exudate may be required. Chronic or serous OM need complex management, possibly surgical.
Complications Complications Intratemporal Intratemporal intratracranial intratracranial Hearing loss Tympanic membrane perforation Mastoiditis Cholestatoma Labyrinthitis others Meningitis Extradural abscess Sudural empyema Brain abscess others http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:33OTr-ilCLStzM:http://de.academic.ru/pictures/dewiki/77/Mastoiditis1.jpg http://t3.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:nwKnADJQFFwfDM:http://www.ferne.org/Lectures/acep_2005_peds/perron_pic_11.jpg http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:UKwRtXWPyE792M:http://top-10-list.org/wp-content/uploads/2009/09/Meningitis.jpg
Reference book Sherris Sherris Medical Microbiology, an Introduction Medical Microbiology, an Introduction to Infectious Diseases to Infectious Diseases. Latest edition, Kenneth Ryan and George Ray. Publisher : McGraw Hill .