Molecular Diffusion in a Controlled Environment
Explore the concept of molecular diffusion in a unique setup where molecules move randomly to achieve homogenization without external factors. Learn about the diffusion equation, Brownian motion, and partial differential equations in physics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
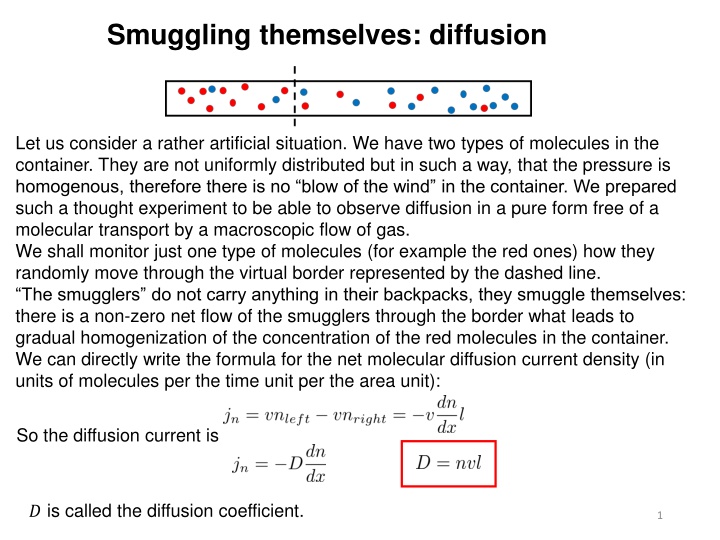
Smuggling themselves: diffusion Let us consider a rather artificial situation. We have two types of molecules in the container. They are not uniformly distributed but in such a way, that the pressure is homogenous, therefore there is no blow of the wind in the container. We prepared such a thought experiment to be able to observe diffusion in a pure form free of a molecular transport by a macroscopic flow of gas. We shall monitor just one type of molecules (for example the red ones) how they randomly move through the virtual border represented by the dashed line. The smugglers do not carry anything in their backpacks, they smuggle themselves: there is a non-zero net flow of the smugglers through the border what leads to gradual homogenization of the concentration of the red molecules in the container. We can directly write the formula for the net molecular diffusion current density (in units of molecules per the time unit per the area unit): So the diffusion current is ? is called the diffusion coefficient. 1
Diffusion equation Outflow from the volume ??: ??? + ?? ??? = John the Baptist equation 2
Partial differential equations of physics Parabolic Hyperbolic Elliptic 4
