Molecular Models for Soda Water Fizzing Activity
In this scientific project, students explore molecular structures and transformations in matter and energy using images and step-by-step activities. The focus is on understanding how atoms bond in molecules, creating reactant molecules like carbonic acid, rearranging atoms to form product molecules like carbon dioxide and water, and comparing photos to understand chemical changes. Through hands-on experiments and visual aids, learners gain a deeper understanding of molecular interactions and chemical reactions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
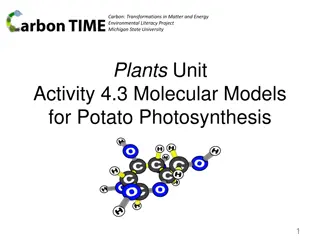
Carbon: Transformations in Matter and Energy Environmental Literacy Project Michigan State University Systems and Scale Unit Activity 3.4 Molecular Models for Soda Water Fizzing 1
Unit Map You are here 2
How Atoms Bond Together in Molecules Atoms in stable molecules always have a certain number of bonds to other atoms: Carbon: 4 bonds Oxygen: 2 bonds Hydrogen: 1 bond Oxygen atoms do NOT bond to other oxygen atoms if they can bond to carbon or hydrogen instead. 3
Making the Reactant Molecules: Carbonic Acid Complete Steps 1 and 2 in Part B of your worksheet. 4
Photo of reactant molecule: H2CO3 (carbonic acid) Chemical change Reactants Products 5
Important: When you are finished constructing the reactants, put all extra pieces away. 6
Rearranging the atoms to make product molecules: Carbon Dioxide and Water Complete Step 3 of Part B of your worksheet. 7
Photo of product molecules: H2O (water) CO2 (carbon dioxide) Start by making the molecules and energy units of the reactants and putting them on the reactants side, then rearrange the atoms and energy units to show the products. Chemical change Reactants Products Remember: Atoms last forever (so you can rearrange atoms into new molecules, but can t add or subtract atoms). Energy lasts forever (so you can change forms of energy, but energy units can t appear or go away) 8
Comparing photos of reactant and product molecules Start by making the molecules and energy units of the reactants and putting them on the reactants side, then rearrange the atoms and energy units to show the products. Chemical change Reactants Products Remember: Atoms last forever (so you can rearrange atoms into new molecules, but can t add or subtract atoms). Energy lasts forever (so you can change forms of energy, but energy units can t appear or go away) 9
What happens to atoms when carbonic acid decomposes? Carbon Dioxide Products Chemical change Carbonic Acid Water Reactants 10
What happens to carbon atoms when carbonic acid decomposes? Carbon Dioxide Products Chemical change Carbon atoms in soda water become part of carbon dioxide molecules. Carbonic Acid Water Reactants 11
What happens to oxygen atoms when carbonic acid decomposes? Carbon Dioxide Products Chemical change Oxygen atoms in soda water become part of water and carbon dioxide molecules. Carbonic Acid Water Reactants 12
What happens to hydrogen atoms when carbonic acid decomposes? Carbon Dioxide Products Chemical change Hydrogen atoms in soda water become part of water molecules. Carbonic Acid Water Reactants 13
What happens to atoms when carbonic acid decomposes? Carbon Dioxide Products Chemical change Atoms last forever! Carbonic Acid Water Reactants 14
Atoms last forever! Compare the atoms in the reactants and the products. 15
Writing a Chemical Equation Chemists use chemical equations to show how atoms of reactant molecules are rearranged to make product molecules Writing the equation in symbols: Chemists use an arrow to show how reactants change into products: [reactant molecule formulas] [product molecule formulas] Saying it in words: Chemists read the arrow as yield or yields : [reactant molecule names] yield [product molecule names] Equations must be balanced: Atoms last forever, so reactant and product molecules must have the same number of each kind of atom Try it: Can you write a balanced chemical equation to show the chemical change when soda water loses its fizz? 16
Chemical equation for soda water losing its fizz H2CO3 H2O + CO2 (in words: carbonic acid yields water and carbon dioxide) 17