Moles and Molar Mass Conversions: Calculations and Formulas
Explore the concept of converting moles to mass and vice versa in chemistry. Learn how to calculate molar masses, determine the number of molecules in a substance, and apply mole-mass conversions to solve practical problems. Discover the molar masses of common substances and grasp the fundamentals of moles and atomic masses.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Moles and Molar Mass Objective: I will be able to convert moles of a substance to mass and mass to moles. Entry Task: The LD50for arsenic (III) oxide, As2O3, is 15 mg/kg. 1. Figure out the lethal dose for a 150 lb adult (1 kg = 2.2 lb) 2. How many molecules do you think are in a lethal dose? What would you need to know to figure this out?
Mass of an atom, mass of a mole of atoms Atomic mass of 1 atom (from periodic table): Mass of C = 12.011 amu Mass of As = 74.922 amu Mass of O = 16 amu Actual mass of 1 mole: Mass of 1 mol C atoms = 12.011 g Mass of 1 mol As atoms = 74.922 g Mass of 1 mol O atoms = 16 g
Mass of molecules Atomic Mass of Molecules (add mass of all atoms): Mass of CO2= 12.011 + 16 + 16 = 44.011 amu Mass of As2O3= 74.922+74.922+16+16+16 = 198.844 amu 1 mol of CO2= 1 mole of C atoms and 2 moles of O atoms 1 mol of As2O3 = 2 moles of As atoms and 3 moles of O atoms Actual mass of 1 mole: Mass of 1 mol CO2= 12.011 + 16 + 16 = 44.011 g Mass of 1 mol As2O3= 74.922+74.922+16+16+16 = 198.844 g
What is the mass of 1 molecule of... PbCl2= 207.2+35.453+35.453 = 278.106 amu 1.01+1.01+16 = 18.02 amu H2O = 12(12.011) + 22(1.01) + 11(16) = 342.352 amu C12H22O11= 40.078+12.011+16+16+16= 100.089 amu CaCO3=
What is the mass of 1 MOLE of... PbCl2= 207.2+35.453+35.453 = 278.106 g 1.01+1.01+16 = 18.02 g H2O = 12(12.011) + 22(1.01) + 11(16) = 342.352 g C12H22O11= 40.078+12.011+16+16+16= 100.089 g CaCO3= Mass of 1 mole of a substance is known as the MOLAR MASS
What are the Molar Masses of: Name of drug Chemical formula Molar Mass Adult dose Moles in adult dose? acetomen -iphen C8H9NO2 500 mg 151.2 g 0.0033 mol 180.2 g aspirin C9H8O4 325 mg 0.0018 mol 206.3 g 0.0019 mol ibuprofen C13H18O2 400 mg
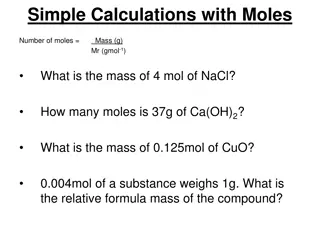
Moles-Mass conversions Mass to moles: # of moles (mol) = mass(g) / molar mass(g/mol) Moles to mass: mass(g) = # of moles(mol) x molar mass(g/mol) 1. I have an 11g sample of Cl2. How many moles do I have? 11g / 70.906(g/mol) = 0.16 mol 1. I have 3.0 moles of MgO. What mass does the sample have? 3 mol x 40.305(g/mol) = 120.915 g
Exit Ticket Methadone is a medication used as a painkiller and as a treatment for those recovering from heroin addiction. The LD50 for methadone is 95 mg/kg. 1. Would you consider methadone to be more or less toxic than acetomenaphen (LD50= 2404 mg/kg)? Than aspirin (LD50= 200 mg/kg)? 2. Explain how you would calculate the amount of methadone that would be lethal to a human.