Montclair CITI New User Instructions
Follow these step-by-step instructions to create a new user account for Montclair CITI program. Learn how to register, provide personal information, choose a username and password, and more to get started with ease.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
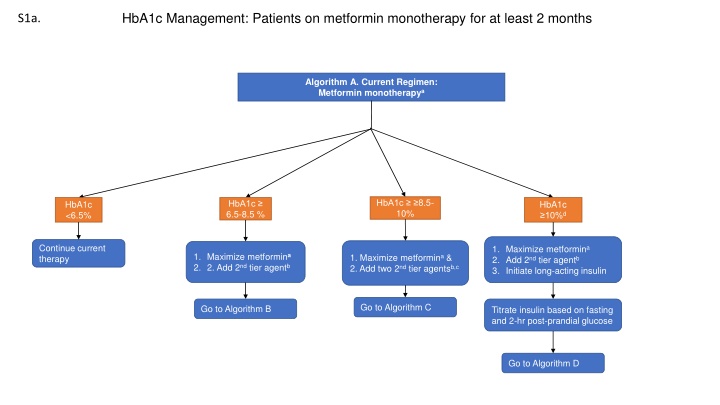
HbA1c Management: Patients on metformin monotherapy for at least 2 months S1a. Algorithm A. Current Regimen: Metformin monotherapya HbA1c 8.5- 10% HbA1c 6.5-8.5 % HbA1c <6.5% HbA1c 10%d Continue current therapy 1. Maximize metformina 2. Add 2nd tier agentb 3. Initiate long-acting insulin 1. Maximize metformina 2. 2. Add 2nd tier agentb 1. Maximize metformina & 2. Add two 2nd tier agentsb,c Go to Algorithm C Go to Algorithm B Titrate insulin based on fasting and 2-hr post-prandial glucose Go to Algorithm D
HbA1c Management: Patients on metformin + additional agent S1b. Algorithm B. Current Regimen: Metformina + 2nd Tier Agent HbA1c 6.5-9% HbA1c 9%d HbA1c <6.5% 1. Maximize current therapya 2. Add a third drug from 2nd tier agentb 3. Initiate long-acting insulin 1. Maximize current therapya 2. Add a third drug from 2nd tier agentb Continue current therapy Titrate insulin based on fasting and 2-hr post-prandial glucose Go to Algorithm C Go to Algorithm D
HbA1c Management: Patients on metformin + 2 additional agents S1c. Algorithm C. Current Regimen: Metformina & Two 2nd tier agents A1c 6.5% A1c >6.5 % Continue current therapy or consider weaning one 2nd tier agent 1. Continue current therapy 2. Initiate long-acting insulin Go to Algorithm D
HbA1c Management: Patients on multiple agents + long-acting insulin S1d. Algorithm D. Current Regimen: Metformina, long-acting insulin & one or two 2nd tier agent(s) A1c A1c <6.5% A1c 7.5-9% A1c 9%d 6.5-7.5 % 1. Continue metformin and 2nd tier agentsb 2. Switch long-acting insulin to degludac 3. Titrate insulin dose as tolerated 4. Consider adding MDI 1. Continue current therapy 2. Add 3rd agent (if applicable)b 3. Titrate insulin dose as tolerated 1. Continue current therapy. 2. Consider weaning insulin 1. Continue metformin and 2nd tier agentsb 2. Switch long-acting insulin to degludac 3. Titrate insulin dose as tolerated
HbA1c Management: Patients on MDI insulin due to initial presumed T1D diagnosis S1e. Algorithm E. Current Regimen: Basal Insulin Bolus Insulin > 6.5-9 % > 9 % <6.5% 1. Add metformin and 2nd tier agentb 2. Stop rapid-acting insulin 3. Do not wean long-acting insulin 1. Add metformin and 2nd tier agentb 2. Stop rapid-acting insulin 3. Wean long-acting insulin, per ISPAD guidelines1 1. Add Metformin, 2. Stop rapid-acting insulin 3. Wean long-acting insulin, per ISPAD guidelines1 References 1. Zeitler P, Fu J, Tandon N, Nadeau K, Urakami T, Barrett T, Maahs D, International Society for P, Adolescent D: ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Type 2 diabetes in the child and adolescent. Pediatr Diabetes 2014;15 Suppl 20:26-46 2. 1. Daniele G, Xiong J, Solis-Herrera C, Merovci A, Eldor R, Tripathy D, DeFronzo RA, Norton L, Abdul-Ghani M: Dapagliflozin Enhances Fat Oxidation and Ketone Production in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016; 3. DeFronzo RA, Inzucchi S, Abdul-Ghani M, Nissen SE. Pioglitazone: The forgotten, cost-effective cardioprotective drug for type 2 diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019 Mar;16(2):133-143. doi: 10.1177/1479164118825376. Epub 2019 Feb 1. PMID: 30706731.