Multi-Core Lock Implementations Overview
Explore a series of lock implementations for multi-core systems, including versions utilizing atomic operations and thread queues. Learn about different approaches to managing locks in parallel processing environments to ensure efficient and safe concurrency control.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
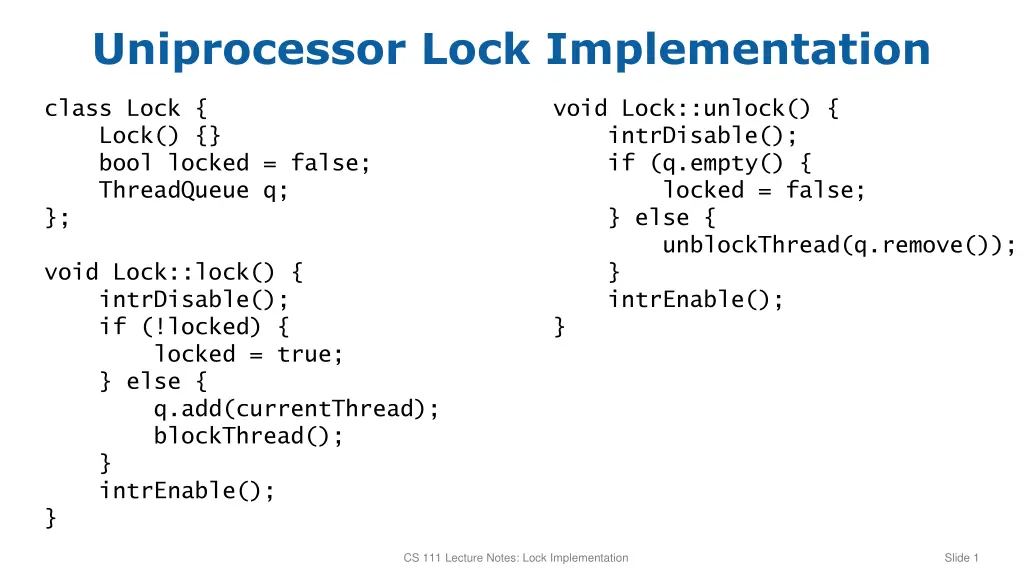
Uniprocessor Lock Implementation class Lock { Lock() {} bool locked = false; ThreadQueue q; }; void Lock::unlock() { intrDisable(); if (q.empty() { locked = false; } else { unblockThread(q.remove()); } intrEnable(); } void Lock::lock() { intrDisable(); if (!locked) { locked = true; } else { q.add(currentThread); blockThread(); } intrEnable(); } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 1
Uniprocessor Lock Implementation?? class Lock { Lock() {} bool locked = false; ThreadQueue q; }; void Lock::unlock() { intrDisable(); if (q.empty() { locked = false; } else { unblockThread(q.remove()); } intrEnable(); } void Lock::lock() { intrDisable(); if (!locked) { locked = true; intrEnable(); } else { q.add(currentThread); intrEnable(); blockThread(); } } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 2
Locks for Multi-Core, v1 class Lock { Lock() {} std::atomic<bool> locked(false); }; void Lock::unlock() { locked = false; } void Lock::lock() { while (locked.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 3
Locks for Multi-Core, v2 class Lock { Lock() {} std::atomic<bool> locked(false); ThreadQueue q; }; void Lock::unlock() { if (q.empty() { locked = false; } else { unblockThread(q.remove()); } } void Lock::lock() { if (locked.exchange(true)) { q.add(currentThread); blockThread(); } } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 4
Locks for Multi-Core, v3 class Lock { Lock() {} bool locked = false; ThreadQueue q; std::atomic<bool> spinlock; }; void Lock::unlock() { while (spinlock.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (q.empty() { locked = false; } else { unblockThread(q.remove()); } spinlock = false; } void Lock::lock() { while (spinlock.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (!locked) { locked = true; spinlock = false; } else { q.add(currentThread); spinlock = false; blockThread(); } } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 5
Locks for Multi-Core, v4 class Lock { Lock() {} bool locked = false; ThreadQueue q; std::atomic<bool> spinlock; }; void Lock::unlock() { while (spinlock.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (q.empty() { locked = false; } else { unblockThread(q.remove()); } spinlock = false; } void Lock::lock() { while (spinlock.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (!locked) { locked = true; spinlock = false; } else { q.add(currentThread); currentThread->state = BLOCKED; spinlock = false; redispatch(); } } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 6
Locks for Multi-Core, v5 class Lock { Lock() {} bool locked = false; ThreadQueue q; std::atomic<bool> spinlock; }; void Lock::unlock() { intrDisable(); while (spinlock.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (q.empty() { locked = false; } else { unblockThread(q.remove()); } spinlock = false; intrEnable(); } void Lock::lock() { intrDisable(); while (spinlock.exchange(true)) { /* Do nothing */ } if (!locked) { locked = true; spinlock = false; } else { q.add(currentThread); currentThread->state = BLOCKED; spinlock = false; redispatch(); } intrEnable(); } CS 111 Lecture Notes: Lock Implementation Slide 7
