Myology: Unraveling Muscle Tissue Types and Functions
Delve into the intricate world of muscle dynamics with this comprehensive guide that explores the diverse types and functions of muscle tissue. Gain a deep understanding of how muscles function and interact within the body, providing invaluable insights into the complexities of movement and physiology. Whether you are a student, athlete, or health enthusiast, this resource offers a valuable exploration of myology and its significance in understanding the human body.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Exploring Myology: Understanding Muscle Dynamics A Deep Dive into Muscle Tissue Types and Functions
Table of content Muscle Mastery Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle: An Overview 01 02 03 Smooth Muscle Characteristics Understanding Cardiac Muscle Muscle Origins & Insertions 05 06 04 Muscle Patterns Muscle Fascia Layers Myology in Medicine 07 08 09
Table of content Muscle Dynamics 10
Muscle Mastery 01 02 03 What is Myology? Muscle Types Functions of Muscles Myology is the scientific study of muscles, focusing on their structure, function, and pathology. Understanding myology is essential for various fields, including medicine, physiology, and sports science. There are three primary muscle types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Each type has distinct structures and functions, playing crucial roles in movement, circulation, and involuntary actions. Muscles perform vital functions such as movement, maintaining posture, and generating heat. They work in coordination with the skeletal system to enable locomotion and support bodily functions. 04 05 Muscle Physiology Applications of Myology Muscle physiology explores how muscles contract and generate force. Key concepts include muscle fiber types, energy sources, and the mechanisms of contraction. Knowledge of myology is applied in rehabilitation, sports, and exercise science. It aids in developing effective training programs and understanding muscle injuries and recovery processes. 01
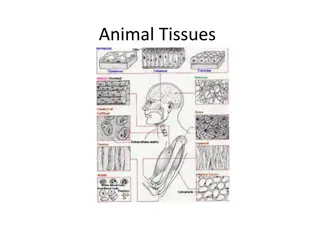
Types of Muscle Tissue Advantages of Muscle Types Disadvantages of Muscle Types Skeletal muscle enables voluntary movement and rapid contraction in response to stimuli. Skeletal muscle can lead to injuries if over-stressed or improperly exercised. Smooth muscle contractions can be slow, affecting response time in certain situations. Smooth muscle functions involuntarily, allowing for control of internal organs without conscious effort. Cardiac muscle has limited regeneration capacity, making heart injuries often severe. Cardiac muscle is highly resistant to fatigue, ensuring continuous contraction for heart function. 01
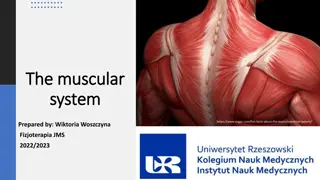
Skeletal Muscle: An Overview 1. Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscles are striated and voluntary, enabling control over movements. They play a vital role in locomotion and posture, contributing to overall body mechanics. 2. Functionality and Importance This muscle type is essential for body movement, facilitating activities such as walking, lifting, walking, lifting, and running, which are crucial for daily life and overall fitness. 3. Structure of Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscles are composed of muscle fibers arranged in bundles. Each fiber contains contains myofibrils made up of sarcomeres, which are the functional units of contraction. contraction. 4. Skeletal Muscle and Health Maintaining skeletal muscle health through exercise and nutrition is vital for preventing preventing injuries and enhancing performance in physical activities.
Smooth Muscle Characteristics Cons of Smooth Muscles Pros of Smooth Muscles Smooth muscles are non-striated, allowing for more flexible contractions. contractions. Smooth muscles can be less responsive to voluntary control compared to skeletal muscles. They control involuntary movements, like digestion and blood vessel regulation. Their slow contraction rate may limit rapid responses in certain situations. Smooth muscles maintain sustained contractions for prolonged periods without fatigue. Smooth muscle disorders can lead to serious health issues like asthma or digestive problems. These muscles are essential for organ functions, coordinating various physiological processes. They tend to heal slower than skeletal muscles, complicating recovery from injuries. 01
Understanding Cardiac Muscle Muscle Type Unique Structure Contraction Rhythm Striated & Involuntary Y-Shaped Fibers Involuntary Energy Source Nucleus Count Single Nucleus Aerobic Respiration 01
Muscle Origins & Insertions 01. Anatomical Overview 02. Muscle Origins Muscles are anchored to bones via tendons. Each muscle has specific origins and insertions that determine its movement and function... The origin of a muscle is its fixed attachment point, point, usually located on the proximal end of the the muscle, serving... 04. Functional Dynamics 03. Muscle Insertions The insertion is the movable end of the muscle, typically attached to the distal bone. It moves towards towards the origin... Understanding origins and insertions is crucial for for comprehending how muscles produce movement, movement, maintain posture, and facilitate various various bodily functions. 05. Clinical Relevance Knowledge of muscle origins and insertions aids in diagnosing injuries, planning rehabilitation, and performing surgical interventions effectively. 01
Muscle Patterns 01. Parallel Arrangement 02. Pennate Arrangement Muscles arranged in parallel exhibit fibers running alongside each other, allowing for greater contraction length and speed. This arrangement is... Pennate muscles have fibers that are angled to the tendon, enhancing force production. This arrangement includes unipennate, bipennate, and multipennate... 03. Sphincter Formation Sphincter muscles are circular in arrangement and control the opening and closing of passages in the body. They play crucial... 01
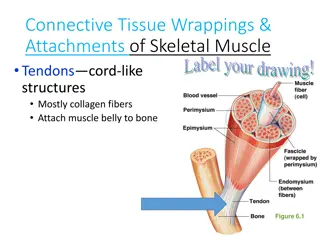
Muscle Fascia Layers 01 03 02 Endomysium Perimysium Fascia Overview Muscle fascia layers consist of three components: endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium, each providing distinct structural support to muscle fibers. The endomysium is the innermost layer, surrounding individual muscle fibers. It provides provides electrical insulation and contributes to contributes to the overall function of muscle contraction. The perimysium envelops bundles of muscle fibers, known as fascicles. It contains blood vessels and nerves, supporting the metabolic and functional needs of muscle tissue. 04 Epimysium The epimysium is the outermost layer of muscle fascia, encasing the entire muscle. It maintains structural integrity and connects muscles to surrounding tissues. 01
Myology in Medicine 01. Muscle Anatomy Basics 02. Surgical Relevance Understanding muscle anatomy forms the foundation for various medical practices, enhancing diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. Knowledge of muscle structure... In surgical procedures, detailed knowledge of muscle muscle anatomy prevents complications and allows for allows for precise interventions, especially in orthopedic and reconstructive... 03. Injection Techniques 04. Rehabilitation Insights Accurate muscle identification ensures safe and and effective injections, minimizing risks of injury to injury to nerves and blood vessels, and enhancing enhancing therapeutic... Myology knowledge helps in designing effective effective rehabilitation programs, facilitating recovery recovery post-surgery or injury by targeting specific specific muscles and improving functional... 05. Professional Training Integrating myology education into medical training empowers future physicians to understand body mechanics, enhancing their competence in various clinical practices... 01
Muscle Dynamics 01. Muscle Function 02. Circulation Support Muscles are essential for movement as they enable the body to perform various activities, from simple gestures to complex athletic... Muscles aid in blood circulation by contracting and relaxing, which helps pump blood and nutrients throughout the body, ensuring all... 03. Organ Functionality 04. Overall Health Muscles support and facilitate various organ functions, allowing for processes like breathing, digestion, and circulation, all crucial for maintaining homeostasis. Maintaining muscle health is vital for overall well well- being, impacting metabolism, strength, and and endurance, which contribute to a higher quality quality of... - 01