Neurotransmitters
Explore the essential role of neurotransmitters as chemical messengers in the body, influencing functions like heartbeat, muscle movements, thoughts, and more. Learn how neurotransmitters work, their actions, and types to understand their impact on various bodily processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
StudyMafia.Org Neurotransmitters Submitted To: Studymafia.org Studymafia.org Submitted By:
Table Contents Definition Introduction Functions of Neurotransmitters Working of Neurotransmitters Actions of Neurotransmitters Types of Neurotransmitters Disadvantages of Neurotransmitters Conclusion 2
Definition Neurotransmitters are your body s chemical messengers. They carry messages from one nerve cell across a space to the next nerve, muscle or gland cell. 3
Introduction Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body can t function without. Their job is to carry chemical signals ( messages ) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell. Your body has a vast network of nerves (your nervous system) that send and receive electrical signals from nerve cells and their target cells all over your body. Your nervous system controls everything from your mind to your muscles, as well as organ functions. In other words, nerves are involved in everything you do, think and feel. 4
Functions of Neurotransmitters Heartbeat and blood pressure. Breathing. Muscle movements. Thoughts, memory, learning and feelings. Sleep, healing and aging. Stress response. Hormone regulation. Digestion, sense of hunger and thirst. Senses (response to what you see, hear, feel, touch and taste). 5
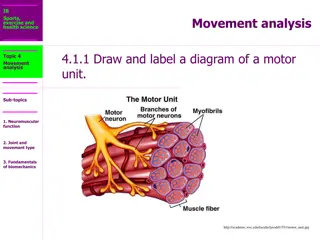
Working of Neurotransmitters A cell body. The cell body is vital to producing neurotransmitters and maintaining the function of the nerve cell. An axon. The axon carries the electrical signals along the nerve cell to the axon terminal. An axon terminal. This is where the electrical message is changed to a chemical signal using neurotransmitters to communicate with the next group of nerve cells, muscle cells or organs. 7
Actions of Neurotransmitters Excitatory. Excitatory neurotransmitters excite the neuron and cause it to fire off the message, meaning, the message continues to be passed along to the next cell. Examples of excitatory neurotransmitters include glutamate, epinephrine and norepinephrine. 8
Actions of Neurotransmitters Inhibitory. Inhibitory neurotransmitters block or prevent the chemical message from being passed along any farther. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine and serotonin are examples of inhibitory neurotransmitters. 9
Actions of Neurotransmitters Modulatory. Modulatory neurotransmitters influence the effects of other chemical messengers. They tweak or adjust how cells communicate at the synapse. They also affect a larger number of neurons at the same time. 10
Types of Neurotransmitters Amino acids neurotransmitters These neurotransmitters are involved in most functions of your nervous system. This is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter of your nervous system. It s the most abundant neurotransmitter in your brain. It plays a key role in cognitive functions like thinking, learning and memory. Imbalances in glutamate levels are associated with Alzheimer s disease, dementia, Parkinson s disease and seizures. 11
Types of Neurotransmitters Monoamines neurotransmitters These neurotransmitters play a lot of different roles in your nervous system and especially in your brain. Monoamines neurotransmitters regulate consciousness, cognition, attention and emotion. Many disorders of your nervous system involve abnormalities of monoamine neurotransmitters, and many drugs that people commonly take affect these neurotransmitters. 12
Types of Neurotransmitters Peptide neurotransmitters Peptides are polymers or chains of amino acids. Endorphins are your body s natural pain reliever. They play a role in our perception of pain. Release of endorphins reduces pain, as well as causes feel good feelings. Low levels of endorphins may play a role in fibromyalgia and some types of headaches. 13
Disadvantages of Neurotransmitters Too much or not enough of one or more neurotransmitters are produced or released. The receptor on the receiver cell (the nerve, muscle or gland) isn t working properly. The otherwise normal functioning neurotransmitter can t effectively signal the next cell. The cell receptors aren t taking up enough neurotransmitter due to inflammation and damage of the synaptic cleft 14
Disadvantages of Neurotransmitters Not enough acetylcholine can lead to the loss of memory that s seen in Alzheimer s disease. Too much serotonin is possibly associated with autism spectrum disorders. An increase in activity of glutamate or reduced activity of GABA can result in sudden, high-frequency firing of local neurons in your brain, which can cause seizures. Too much norepinephrine and dopamine activity and abnormal glutamate transmission contribute to mania. 15
Conclusion Neurotransmitters play a role in nearly every function in your body. More specifically, neurotransmitters are the chemical communicators that carry a nerve s message from one nerve cell to the next cell. Without neurotransmitters, your body can t function. Too high of a level or too low of a level of specific neurotransmitters results in specific health problems. 16
References Google.com Wikipedia.org Studymafia.org Slidespanda.com
Thanks To StudyMafia.org