Non-Conventional Energy Sources and Optical Fiber Overview
Dr. R. R. Mistry presents insights on non-conventional energy sources like wind, solar, and geothermal energy along with an introduction to optical fiber technology focusing on fabrication and cables.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Topic Non-Conventional Energy Sources and Optical Fiber Presented by Dr. R. R. Mistry Asst. Professor Department of Physics Deogiri College, Aurangabad
Chapter 1. Non-conventional Energy Sources Introduction, energy, tidal energy/Ocean energy, geothermal energy, biogas, hydro energy, wind energy, solar energy, biogas plant-fixed dome type. Biomass, wind
Wind energy: Introduction to wind energy, terms and definition: wind, wind farm, wind turbine, vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT), horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT), (wheel), wind mill, types of wind turbines generator units, monoblade HAWT, twin blade HAWT, merits and limitation of wind energy. propeller
Chapter 2. Solar Photovoltaic Systems:- Introduction to photovoltaic systems, Solar Cell fundamentals: i)Semiconductor, ii)P-N junction, iii)Generation of electron-hole pair by photon absorption, iv)I-V characteristics of solar cell. Electrical Storage: Lead acid battery, basic battery theory.
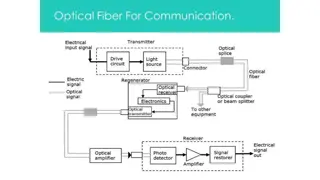
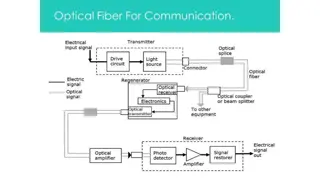
Chapter 3. Introduction of Optical Fiber Introduction, importance of optical fiber, classification of optical fiber stepped index fiber, stepped index monomode fiber, disadvantages of monomode fiber, plastic fiber, latest developed types of HPSUV; HPSIR; Halide; Tapered. optical fibers
Chapter 4. Fiber Cables and Fabrication Fiber fabrication: Classification of fiber fabrication techniques; external vapour deposition (external CVD), axial vapour deposion internal chemical deposition (internal CVD). chemical (AVD), vapour
Fiber Cables: Construction, Strength members, cable tensile loading, minimum bend radius losses incurred during installation of cables or during subscriber service testing of cable, selection criteria optical cable fiber laying in telephone.
Chapter 1. Non-conventional Energy Sources Introduction:- The energy demand is increasing in day by day due to rapid industrialization and population growth. The conventional sources of energy will not be sufficient to fulfill the growing demand.
Conventional sources like fossil fuel and nuclear causes pollution and it become crisis in future. Non-Conventional energy sources are available in nature free of cost. There are abundant renewable sources of energy such as wind, sun, water, sea, biomass apart from even daily wastes. These sources are pollution free and clean energy.
Biomass Energy:- The energy obtained from biomass is known as biomass energy.
Biomass most often refers to plants or plant-based materials, which can be utilized in a wide variety of forms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly via combustion to produce heat, or indirectly after converting it to various forms of bio-fuel. Historically, biomass energy has been associated with burning wood, peat, dung, etc. for generating heat. There was a time when biomass in the form of wood was the primary fuel for heating and cooking around the world. Currently, the term is used to capture a variety of fuels and techniques to convert them to energy. The primary of these are:
Direct application for cooking and heat. Although this is not a significant source of energy in the United States, it is still a common practice in developing countries. Electric generation: Biomass is burned in a boiler to heatwateras is done with fossil fuels. Gassification: Biomass is heated to release biogas, which is primarily methane and carbon dioxide. The biogas is then burned, which converts the methane to carbon dioxide and water, and the heat is used to boil water as in a typical gas-fired steam electrical generation plant. burning: This is the traditional
Anaerobic Digestion: Similar to gasification in which biomass is fermented to convert the organic materials into biogas. Typically, enzymes orcatalysts are used to enhanceconversion. Conversion to Bio-fuels: Biomass, primarily in the form of vegetable oil, is converted to liquid fuel, most commonly ethanol and biodiesel, for use in transportation. Conversion to hydrogen: Biomass is converted to biogas, which can then be processed to strip out the hydrogen for use in hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, e.g., foruse in an electric car.