Nuclear Angular Momentum in Atoms: Quantum Numbers and Spin
Explore the quantum numbers and spin related to nuclear angular momentum in atoms, including the principles of electron orbitals, orbital angular momentum, magnetic quantum numbers, and spin concepts. Gain insights into the total angular momentum and nuclear spin in atomic structures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
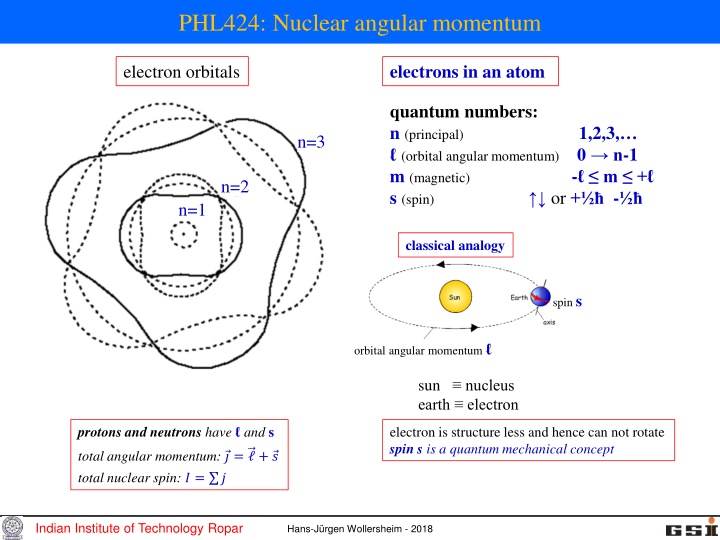
PHL424: Nuclear angular momentum electrons in an atom electron orbitals quantum numbers: n (principal) 1,2,3, (orbital angular momentum) 0 n-1 m (magnetic) - m + s (spin) or + - n=3 n=2 n=1 classical analogy spin s orbital angular momentum sun nucleus earth electron protons and neutrons have and s electron is structure less and hence can not rotate spin s is a quantum mechanical concept total angular momentum: ? = + ? total nuclear spin: ? = ? Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Nuclear spin quantum number protons and neutrons have orbital angular momentum and spin s total angular momentum: ? = + ? total nuclear spin: ? = ? ? = ?1+ ?2+ ??, ?1+ ?2+ ?? 1, , ?1 ?2 ?? quantum mechanics Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Nuclear spin quantum number protons and neutrons have orbital angular momentum and spin s total angular momentum: ? = + ? total nuclear spin: ? = ? ? = ?1+ ?2+ ??, ?1+ ?2+ ?? 1, , ?1 ?2 ?? quantum mechanics 1H = 1 proton, so I = 2H = 1 proton and 1 neutron, so I = 1 or 0 For larger nuclei, it is not immediately evident what the spin should be as there are a multitude of possible values. mass number number of protons number of neutrons spin (I) example even even even 0 16O odd odd integer (1,2, ) 2H odd even odd half-integer ( 2, ) 13C 3 12, odd even half-integer ( 2, ) 15N 3 12, Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Nuclear spin quantum number The magnitude is given by ? = ? ? + 1 The projection on the z-axis (arbitrarily chosen), takes on discretized values according to m, where ? = ?, ? + 1, ? + 2, ,+? Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Parity wave particle duality: photoelectric effect wave function (x) (x) = (-x) parity = even (+) x (x) = 0, 2, 4, even x (x) = - (-x) parity = odd (-) = 1, 3, 5, odd Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Magnetic moment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Magnetic_moment.svg/200px-Magnetic_moment.svg.png ? = ? ? A ? =2?? ? =2?? media/image3.jpeg = ??? ? ? ? =? ? 2?? ? =? ? 2?? ??2=? ? ? I ? =? ? 2 ? =? ? ? ??? ? ??? ?=? ??? ?=? 2 2?? 2?? ? = ?? electron orbital magnetic moment ? = ?? ??=? proton orbital magnetic moment 2?? Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Magnetic moment ? = ?? electron orbital magnetic moment ??= 2.0023 ?? ? electron spin magnetic moment (Dirac equation) ??= +5.585691 ?? ? proton spin magnetic moment ??= 3.826084 ?? ? neutron spin magnetic moment Why has a neutron a magnetic moment when it is uncharged? Bildergebnis f r proton chemie Bildergebnis f r neutron u-quark: + d-quark: 2 3? 3? neutrons and protons are not elementary particles internal structure: they have charges. 1 proton +1e neutron 0e 2? = 5.59 3.83 ?? 1 = 0.8574 ?? ?? 1 2= 0.87980?? (experiment) Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ??= +5.585691 ?? ? proton spin magnetic moment gyromagnetic ratio ? = ? ?? = ? 47.89 106 ? 1? 1 ??= ? ? proton ?-factor: +5.585691, spin I: proton in magnetic field energy difference between states ? = ? ? = 2 ?? ?0 ? Larmor frequency ? = 2? ?0 ? for proton ??? 2?= 42.57 ? Larmor frequency low energy high energy low energy high energy Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Hans-J rgen Wollersheim - 2018