Oedogonium Reproduction Methods and Sexual Differentiation
Learn about the reproduction processes in Oedogonium, including vegetative, asexual, and sexual methods. Explore the development of zoospores, oogamous sexual reproduction, and the categorization of Oedogonium species based on sex organ distribution. Detailed explanations and images included.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Oedogonium: : Reproduction Reproduction Dr. Jahid Ali Malik
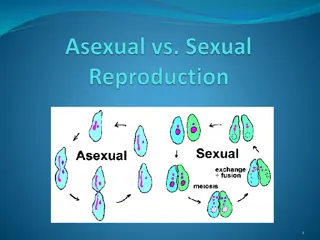
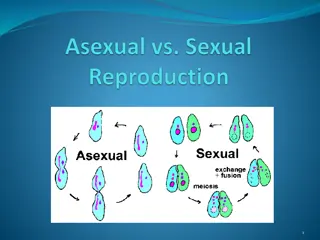
The reproduction in Oedogonium occurs by i. Vegetative, ii. Asexual and iii. Sexual methods
Vegetative Reproduction: By fragmentation: The filament may get broken into small fragments. Each fragment grows into new filament. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: (a) By Zoospores During normal favourable conditions the alga reproduce by the formation of zoospores. Each mature zoospore is spherical or pear-shaped. It is multiflagellated and possesses a crown of short flagella in ring at its Colourless anterior end.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Sexual reproduction is of oogamous types. The female sex organ is oogonium The male sex organ is antheridium On the basis of distribution of sex organs, Oedogonium are grouped under the following categories (1) Macrandrous species (2) Nannandrous species
(1) Macrandrous species: In this case the male and female filaments are morphologically similar. The antheridia are borne on the normal filament. may be of the following types- (a) Monoecious species: The antheridia and oogonia develop on the same filament. (b) Dioecious species: In this case the antheridia and oogonia are borne on different filaments
A. Macrandrous monoecious species showing antheridia and oogonia in the same filament. B-C. Macrandrous dioecious specics showing oogonia and antheridia in different filaments
(1) Nannandrous species: Nannandrous species are dioecious and exhibit dimorphism. The antheridia are borne on a special small few celled filament, called nannandrium or 'dwarf male . There are two kinds of nannandrous species- (a) Gynandrosporous: Both oogonia and androsporangia are borne on the same filament. (b) Idioandrosporous: The oogonia and androsporangia are borne on separate filaments.
A. Nannandrous gynandrosporous sp B-C. Nannandrous idioandrosporous sp
Thank You Thank You