Ovarian and Reproductive System Disorders
Inflammation of the ovary, cystic Graafian follicles, granulosa cell tumors, and hydrosalpinx are some conditions affecting the female reproductive system. Oophoritis, cyst formation due to hormone deficiency, tumor development, and fallopian tube blockages can impact fertility and health. Understanding these disorders is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment to maintain reproductive well-being.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
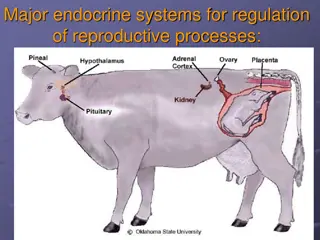
Female Reproductive system by: dr. yasmeen jasim
Ovaries Oophoritis Oophoritis which means ?nflammation of the ovary, commonly due to an infection. which is inflammation and infection in the upper genital tract of females. Infection ascends from bacterial colonization of the cervix and extends to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and the ovary. Gonorrhea and Chlamydia typically are colonized from the cervix in cases of oophoritis, but these pathogens are rarely isolated in ovarian tissue. Rather, these organisms facilitate other bacteria to infect the adnexa. If left untreated, an abscess may form around the fallopian tubes and ovary, known as a tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA).
Microscopically, the lesion ranges from focal necrosis and mononuclear cell infiltration to diffuse haemorrhage and necrosis.
Cystic Graafian follicles Cystic Graafian follicles : occur when a graafian follicle does not rupture but rather persists for a variable period of time.And Cysts are formed due to luteinizing hormone deficiency. This condition is important in cows because it leads to a prolongation of the postpartum period of the first estrus and ovulation does not occur. In cows, the diameter of the cystic follicles ranges from 2.5-3 cm and remains for a period of ten days or more without the formation of the corpus luteum. Cystic follicles may be single or multiple, unilateral or bilateral and thin-walled.
Microscopically, the granular layer is thicker than normal or degenerative, and ultimately becomes flat and in the form of a single layer of cells, without evidence of corpus luteum formation.The surrounding theca is thin. follicle cyst is lined by an inner layer of attenuated or stratified granulosa cells and an outer layer of theca cells. may show luteinization.Fluid is clear or hemorrhagic.
Granulosa cell tumors Granulosa cell tumors are the most common in the ovaries of large animals. These tumors are unilateral, with a smooth, rounded surface and a diameter of 20-30 cm. They can be cystic or multi-cystic, and the fluid inside the cysts is usually red.
Uterine tubes Hydrosalpinx: is a condition where fluid accumulates in one or both fallopian tubes, creating a blockage. Hydrosalpinx can be caused by an old infection in the fallopian tubes, sometimes a sexually transmitted infection. Other causes (particularly surgeries on the tube), severe adhesions of your pelvis,and endometriosis, include previous surgery
The resulting expansion can be regular or irregular and the wall is thin with an increase in the length of the tube,which increases its tortuosity Salpingitis Salpingitis :is inflammation of the fallopian tubes, caused by bacterial infection. Common causes of salpingitis include sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhoea and chlamydia. Salpingitis is a common cause of female infertility because it can damage the fallopian tube.
Grossly: The lesion cannot be seen except for hyperemia, thickening of the mucus, and the presence of a small amount of exudate in the cavity. Microscopically: Inflammation ranges from mild to severe and from acute to chronic. Regardless of its severity, inflammation impairs fertility. Initially, there is a loss of cilia and desquamation of epithelial cells at the tops of the mucosal fold. In severe cases, the inflammation includes the muscular layer, and the cavity contains an amount of exudate, with the presence of adhesions between the spaces that have lost their epithelium, and the adjacent mucosal spaces become either cystic or connective tissue.
Pyosalpinx Pyosalpinx or tubal abscess is an obstruction of the Fallopian tube, resulting in pus accumulation, which commonly results from the spread of bacteria from the lower genital tract. It is a serious complication from untreated or inadequately treated acute pelvic inflammatory disease associated with high morbidity. Microscopically, a large number of neutrophils as well as other types of inflammatory cells are observed inside the tissues and in the mucous cysts, and squamous metaplasia of the epithelium may be observed.
Uterus Metritis Metritis :the inflammation of uterus characterized by suppurative exudate, hemorrhage and necrosis of uterus. Etiology Actinomyces pyogenes E.coli Staphylococci Streptococci Trichomonas foetus Campylobacter foetus.
Macroscopic and microscopic features Congestion,catarrhal or purulent exudate Hemorrhage Enlargement,oedema Oozing out of pus from uterus on pressure Seropurulent exudate in uterine wall. Infiltration of macrophages and lymphocytes Desquamation of lining epithelium
Pyometra Pyometra is an acute or chronic suppurative inflammation of uterus resulting in accumulation of pus in the uterus. Etiology Occurs under the influence of progesterone. E. coli Actinomyces pyogenes Proteus spp. Staphylococcus aureus Trichomonas foetus
Macroscopic and microscopic features Discharge of thin cream like pus from vulva soiling the tail and perineal region. Enlargement of abdomen due to distension of uterus. Uterus looks like a pregnant uterus as a result of accumulation of pus. This condition is also known as pseudopregnancy. Rention of lutein cyst. Congestion, infiltration of neutrophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells. Necrosis of mucosal epithelium of uterus. Proliferation of endometrial epithelium ( cystic hyperplasia )
ENDOMETRITIS Endometritis is the inflammation of endometrium, the mucosa of uterus. It may be catarrhal or purulent and may occur after metritis. Etiology Trichomonas foetus Campylobacter foetus Staphylococci
Macroscopic and microscopic features Catarrhal desquamated cells. Congestion Moderate infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils in mucosa discharge from uterus containing
Vaginitis Vaginitis : the inflammation of vagina characterized by congestion, granularity as a result of elevations in mucosa. Etiology Mycoplasma bovigenitalium Bovine herpes virus-1 (BHV -1) Picorna virus Trichomonas foetus Macroscopic and microscopic features Granular elevation in vaginal mucosa. Congestion Prolapse Accumulation of lymphocytes in sub epithelial region
Vulvitis Vulvitis is inflammation of vulva, or genitals. Vulvitis is common and can result from an allergic reaction, an infection or an injury. Symptoms include itching, redness and swelling in vulva. may also have an abnormal vaginal discharge. A granular vulvitis The acute form of the disease was characterized by a purulent vulvar discharge, an inflamed hyperemic vulvar mucosa granularity.In the chronic form,there was an absence of a purulent discharge and a gradual decline in the severity of the hyperemia and granularity. Epithelial inclusion cysts were observed in the vulvar epithelium of approximately 10% of affected cows. and varying degrees of
Dourine disease Dourine disease is a chronic or acute contagious disease of breeding equids that is transmitted directly from animal to animal during coitus. isTrypanosoma (Trypanozoon) equiperdum. T.equiperdum can pass through intact mucous membranes of reproductive Tract,stays initially at the mucosal surface and subsequently invade tissues, giving oedematous plaques in genitalia, and ulceration of mucosa. It can also reach the blood stream and therefore other areas of the organism. The causal organism
Tumors of female genital system Endometrial carcinoma Endometrial polyps Fibroma . Hemangioma Luteal cell tumor . leiomyoma . Lymphosarcoma ovarian teratoma ovarian adenocarcinoma Papillary Adenocarcinoma .