Overview of Kidney Function Tests: Diagnosing Disorders
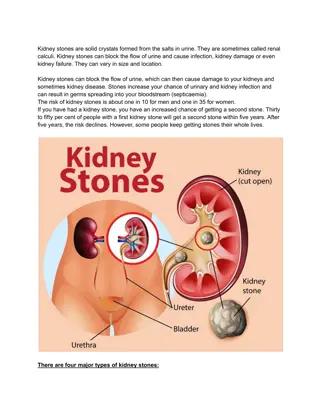
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron, and urine formation involves processes like glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. Kidney function tests aim to diagnose kidney diseases, urinary tract disorders, and systemic conditions affecting kidney function. These tests include macroscopic, microscopic, and chemical examinations of urine. Learn about the significance of color, odor, pH, specific gravity, and volume in urine analysis. Understand how abnormalities in these parameters can indicate various health issues.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Role of the Insurance Broker in Business Key Criteria and Considerations Justin Lord and Amy Head HUB International
What is an Insurance Broker? What is an Insurance Broker? Why are there insurance brokers? Role of a broker vs. agent
Benefits of using a broker Why You Why You Need an Need an Insurance Insurance Broker Broker Industry Knowledge Risk Assessment Tools for risk management Access to multiple insurance options Some markets are only accessible through a licensed agent
Types of Insurance Brokers Types of Insurance Brokers Independent brokers vs. Agencies Specialization Market size Geography Industry
Common reasons a corporation may release an RFP for broker services Lack of communication Lack of team depth or execution on key services Errors on policy or pricing Mandatory RFP process due to internal policy General Dissatisfaction Change in support staff Why are you Why are you looking looking for/replacing for/replacing a Broker? a Broker?
Personal vs. Business Insurance Needs Personal vs. Business Insurance Needs Key differences in choosing a broker for personal vs. business purposes
Broker Scope of Services needed Identifying Identifying Your Your Level of ongoing support needed Insurance Insurance Needs Needs Level of expertise needed Property Liability Employee Benefits Coverage types
Commercial Commercial and Property vs. and Property vs. Employee Employee Benefits Benefits Insurance Insurance Key differences in choosing a broker for P&C and EB Stakeholders Decision Makers Calendar Support Needs Needs
Common Insurance Mistakes Common Insurance Mistakes Underinsuring Overinsuring Overlooking key areas of coverage Overlooking gaps in coverage Treating Insurance as a commodity Not understanding the risk you are trying to manage
Trustworthiness Qualities Qualities to Look For to Look For Experience Industry knowledge Strong Team Structure
Licensing and Certifications Licensing and Certifications Importance of proper credentials and state licensing Relevant industry certifications: Certified Employee Benefit Specialist The CEBS designation delivers benefits expertise supported by research-based best practices with a curriculum developed by the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania and administered by the International Foundation of Employee Benefit Plans Chartered Property Casualty Underwriter (CPCU) Considered the industry standard, this designation is for those who specialize in property-casualty insurance and risk management. It can help agents gain knowledge of underwriting, risk selection, legal issues, and more. Certified Insurance Counselor (CIC) This respected certification is earned by completing a series of courses and exams on insurance, risk management, and agency operations. Associate in Risk Management (ARM) This designation is for insurance professionals who have developed a deeper knowledge of risk elements. Certified Risk Manager (CRM) This designation is for financial professionals with training in risk management. It's important for risk managers in finance, insurance, accounting, and legal fields.
Experience Experience in Your in Your Specific Specific Insurance Insurance Type Type Experience in EB vs. commercial insurance Specialization in niche industries or coverage areas Experience in multiple funding mechanisms and cost containment strategies Experience with a variety of Industry and population types
Ability to Understand Your Needs and Respond Ability to Understand Your Needs and Respond Ability to assess client risk, population, past challenges and create a strategy to engage with all of these Ability to Ability to create a service calendar and deliverables communicate with variety of stakeholders Ability to customize an approach
Access to a Wide Network of Insurers Access to a Wide Network of Insurers Larger client bases gives more leverage to the broker and by extension their clients Brokers with access to multiple insurers offer more choices Connections to carriers at a leadership levels allow escalation when necessary Competition is important, though Marketing needs to be executed strategically
Ability to explain policies and terms clearly Strong Strong Communication Communication Skills Skills Regular and transparent communication Multi-Channel approach to communication with client population
Attention to Detail Attention to Detail Ensuring that nothing is overlooked Careful review of policies Linear thinking versus conceptual thinking Need for both in risk assessment Need for both in execution
Research and Referrals vs. RFP Process Research and Referrals vs. RFP Process Start by asking for recommendations from trusted sources Use online reviews, testimonials RFP for Broker Services
Check Credentials Check Credentials Verify licensing and certifications through official channels Check for disciplinary actions or complaints
Request References Request References Contact Require Understand Understand they will likely be sources that have been pre-vetted Don t hesitate Don t hesitate to ask the reference about both positive and negative experiences Contact current or past clients for feedback on their experience Require potential brokers to offer client references
Prepare questions to assess the broker s knowledge and fit Conduct Interviews The RFP process can narrow the choices Finalist Meeting Stakeholders
Comparison of potential brokers Cost Structure Service Model Access Agency Culture/Reputation Differentiating Brokers
Assess the Service Level/Structure Setting Expectations Who will provide post-sales service? Annual Service timeline/calendar Cadence of interactions Scheduled Meetings vs. Ad Hoc Meetings
Review the Brokers Insurer Access Assess the number and reputation of the insurance companies the Brokers works with Ask about National or Corporate partnerships Ask about Blocks of Business Ask About Experience with multiple funding models Ask about Industry or Specialty markets
Do you specialize in any specific size, industry, or funding type? Coverage- Related Questions Can you explain my coverage options to a variety of people in my organization? Which insurance companies do you work with most frequently? Why?
What level of support can I expect post-sale? Service- Related Questions What is my service team structure? Will the selling agent still be my mine point of contact? Claims Support Billing Support Renewal Support Vendor Relationship Issues Who do I contact for :
Is it negotiable? Is the agreement multi-year? How is your compensation structured? Service- Related Questions Are there additional fees I should be aware of? Do you get additional compensation/overrides for placing business with specific vendors?
How often will we review and market lines of coverage? Who will present these options? What stakeholders should be involved? Renewal and Policy Review How often will we review benchmarking? How often will we review performance analysis? Do you have tools to anticipate market trends/claims performance?
What analytic tools do you provide? What Open Enrollment support do you provide? Value Do you offer compliance tools? Adds/Scope of Service Do you offer technology and HR tools? Do you offer other tools for member support? Is there additional cost for your tools?
Importance of not just choosing based on the lowest price Comparing Cost vs. Value The value of building a long-term partnership A consultative versus transactional approach
Balancing expertise, service model, and price to make a choice Making an Stakeholders in the decision Informed Decision Pre-existing relationships Expertise and delivery versus personal rapport
Push Lead Seem Leverage Red Flag 1 Pushy Sales Tactics Push unsuitable or unnecessary coverage Lead with how much savings they will provide without analysis Seem to push a single solution or vendor Leverage outside relationships to pressure a change in vendor or brokerage
Red Flag 2 Lack of Transparency Difficulty in explaining terms or reluctance to share full information Unwilling to share compensation model Always find a way to maintain incumbent vendors
Brokers who exclusively work with only one or two insurers Red Flag 3 Limited or Highly Specific Market Access Limited geographic reach Limited resources outside direct local policy support Try to impose market solution from another region of their practice
Red Flag Poor reviews or unresolved complaints from current client 4 Negative Client Feedback Unwillingness to support a transition in client/broker relationship Consistently short client tenure
Red Flag 5 Bad Communication Failure to respond to issues when directly approached Unreasonably long delays in response time Push difficult conversations to subordinates Makes promises but fails to execute
Why you need a broker Understand your specific needs Summary of Key Points Qualities of a good broker Expertise, experience and strong reputation Works with wide array of carriers and vendors Deep team/support structure Steps in Evaluation Avoid Red Flags
Thank you! Thank you! Q&A Q&A