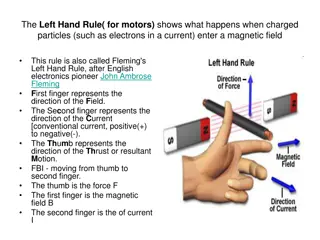
Overview of Revised Final Rule for Human Subject Research
Revised Final Rule for Human Subject Research outlines key dates, exemptions, and applicability under Subparts A, B, and C. The rule aims to modernize oversight, with a compliance date of January 21, 2019. Updates on exempt research categories, including limited IRB review and broad consent, are highlighted. Research involving pregnant women, fetuses, neonates, and prisoners is discussed.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pneumatic retinopexyversus scleral buckle for repairing simple rhegmatogenousretinal detachments Elham Hatef, Dayse F Sena, Katherine A Fallano, Jonathan Crews, Diana V Do Issue 5, 2015 A presentation to: Meeting name Date Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health.
Table of Contents 01 Background 02 Typesof studies 03 Key results 04 Tables (Risk of Bias/Forest Plots) 05 Conclusions 06 Acknowledgements
01: Background Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RDD) is a break in the sensory retina, caused by traction on the retina Pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckle, and vitrectomy are all accepted treatments for RDD Objective: to assess the effectiveness and safety of pneumatic retinopexyversus scleral buckle or pneumatic retinopexy versus a combination treatment of scleral buckle and vitrectomy for people with RRD
02: Types of studies Participants 218 eyes of 216 participants Interventions Pneumatic retinopexy VERSUS Scleral buckle
03: Key results Both studies showed fewer eyes achieving retinal reattachment in the pneumatic retinopexygroup compared with the scleral buckle group by six-months follow-up RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.02; 218 eyes Eyes in the pneumatic retinopexygroup also were more likely to have had a recurrence of retinal detachment by six-months follow- up RR 1.80, CI 1.00 to 3.24, 218 eyes
04: Tables Reattachment of the retina at 6 months follow-up
04: Tables Recurrence of retinal detachment through 6 months follow- up
04: Tables Adverse events through 6 months follow-up
05: Conclusions pneumatic retinopexymay result in lower rates of reattachment and higher rates of recurrence than scleral buckle for eyes with RRD, but does not rule out no difference between procedures.
06: Acknowledgements Cochrane Eyes and Vision US Satellite, funded by the National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health Cochrane Eyes and Vision Editorial Base, funded by the UK National Health Service Research and Development Programme Elham Hatef, Dayse F Sena, Katherine A Fallano, Jonathan Crews, Diana V Do Review citation HatefE, SenaDF, FallanoKA, Crews J, Do DV. Pneumatic retinopexy versus scleral buckle for repairing simple rhegmatogenous retinal detachments. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 5. Art. No.: CD008350. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008350.pub2