Overview of Sulphonamides: Classification and Uses
Sulphonamides, also known as sulpha drugs, are synthetic chemical agents derived from Para amino benzene sulphanilamide (PABS). This group of drugs opened a new era of chemotherapy when discovered in 1939. Common drugs in this class include Sulphacetamide, Sulphadiazine, and Sulphaguanidine, each with unique properties and uses. Sulphonamides are classified into Sulpha drugs, Folate reductase inhibitors, and Sulphones, each serving specific medical purposes. Explore the chemical structures, properties, and applications of these important drug agents.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
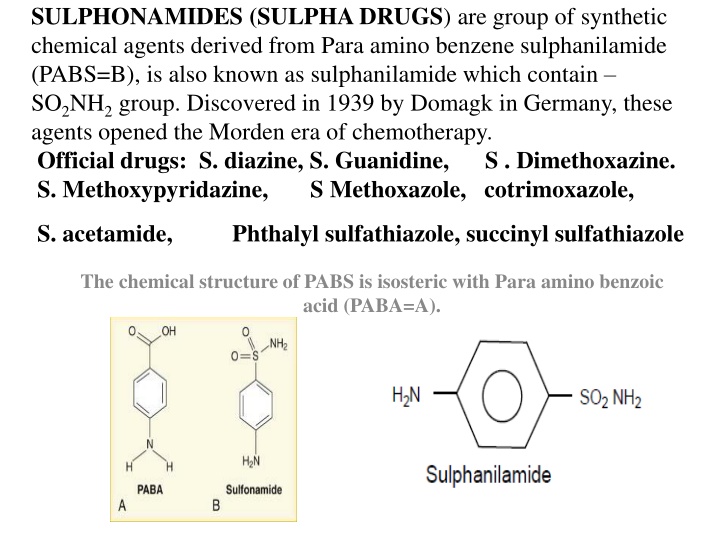
SULPHONAMIDES (SULPHA DRUGS) are group of synthetic chemical agents derived from Para amino benzene sulphanilamide (PABS=B), is also known as sulphanilamide which contain SO2NH2group. Discovered in 1939 by Domagk in Germany, these agents opened the Morden era of chemotherapy. Official drugs: S. diazine, S. Guanidine, S . Dimethoxazine. S. Methoxypyridazine, S Methoxazole, cotrimoxazole, S. acetamide, Phthalyl sulfathiazole, succinyl sulfathiazole The chemical structure of PABS is isosteric with Para amino benzoic acid (PABA=A).
CLASSIFICATION I. Sulpha drugs: S. Acetamide S. Diazine, S. Guanidine, S Dimethoxazine. S. Methoxypyridazine S. Methoxazole, Phthalyl Sulfathiazole, Succinyl Sulfathiazole, Cotrimoxazole, II. Folate reductase inhibitors-Trimethoprim, Co-trimoxazole III.Sulphones: Dapsone, Acetapsone, Solapsone
1. SULPHACETAMIDE (Albucid, isoptocetamide) Nomenclature: N-[(4-aminophenyl)-sulphonyl]-acetamide properties: white or yellowish white prisms, acidic, slightly saline taste; soluble in water, alcohol, acetone, soluble in mineral acids and alkali hydroxides and carbonated, slightly soluble in ether, very soluble in chloroform. Uses: It is topically approved in the treatment of acne and Seborrheic dermatitis; orally for urinary tract infection (UTI). preparations: Sulphacetamide 10% topical lotion; Sulphacetamide sodium salt powder, eye drops 10%; 20%; 30% w/v and eye ointment 5% and 10% w/v. Sulphacetamide Eye Drops IP, BP
2. SULPHADIAZINE (Diazin, Debenal) Nomenclature: 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl benzene sulphonamide Properties: White or slightly yellow powder; sparingly soluble in water, alcohol, acetone, freely soluble in dilute mineral acids, soluble in potassium and sodium hydroxides MP: 252-256oC Uses: Commonly used to treat UTI, in combination with pyrimethamine used to treat toxoplasmosis infection. Dose: Initial oral dose, 3 gram and subsequently, up to 4 gram daily in divided doses. Preparations: Sulphadiazine tablets IP, Sulphadiazine injection, BP [NOTE]: Silver Sulphadiazine is a silver salt, effective topical anti- microbial agents used in pseudomonas infection for burn therapy
3. SULPHAGUANIDINE (Guanicil) Nomenclature: N-(P-aminobenzenesulphonyl) guanidine Properties: white, fine crystalline powder. It is very slightly soluble in water and in alcohol it dissolves in dilute mineral acids. It should be protected from light. MP: 185-189OC Dose: orally, 6-12gram daily divided doses Uses: it is poorly absorbed orally. Used in combination with other drugs, usually in the treatment of GI tract infection Such as intestinal infection, especially for bacillary dysentery, it is also used externally to the skin and throat. Preparations: Suphaguanidine IP, Suphaguanidine Tablet IP
4. SULPHA DIMETHIAZINE (Sulphadimidine) Nomenclature 4-amino-N-(4, 6 dimethyl-2-pyrimidinyl) benzene sulphonamide Properties: White to yellowish odorless crystals, having bitter tastes; very slightly soluble in water and in ether, slightly soluble in alcohol and soluble in acetone. Affected as darken on exposure to light. Dose: 5-10 gram/daily in divided doses Uses: Antibacterial agents for mainly UTI caused by susceptible microorganisms Preparations: Sulphamethiazine Tablets