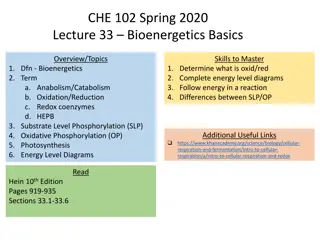
Oxidation and Reduction in Biotechnology through Erasmus+ Sustainability
Explore the concept of oxidation and reduction in biotechnology with the help of Erasmus+ Sustainability, discussing electron donation, electron acceptance, oxidation numbers, and calculation examples. Learn how these processes work together for sustainable biotechnological applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Erasmus+ Sustainability by Biotechnology Oxidation and Reduction Ren e Ristl Evelin Szabados
Definition Oxidation: electron donation Reduction: electron acceptance Example: Oxidation: 2 O2- O2 + 4 e- Reduction: Fe3+ + e- Fe2+ Both, oxidation and reduction have to occur together!
Oxidation numbers Often there aren t real molecular charges e.g. glucose or water Atoms possess an oxidation state, described by oxidation numbers H2, O2 are neutral oxidation number 0 In water (H2O), the H has got the oxidation number +1, the O: -2 In organic compounds, the oxidation number of C has to be calculated
Calculation: Oxidation number of C E.g. glucose: + 1 -2 + 1 +1 2 = -1 C is neutral it needs +1 to equalise
Examples +1 0 Oxidation: 2 H2 4 H+ + 4 e- Together: 2 H2+ O2 2 H2O -2 0 Reduction: O2 + 4 e- 2 O2- +3 +1 Oxidation: + 2 e- R R