Pathology of Diabetes Mellitus: Understanding the Complications
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by inadequate insulin action, leading to various complications affecting different organs. Learn about the pathology, definition, measurement, insulitis, metabolic actions of insulin, pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, and complications such as atheroma, hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ENDOCRINE BLOCK Lecture 1 and 2: Lecture 1 and 2: Pathology of Diabetes Pathology of Diabetes Mellitus Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is an extremely common metabolic disorder, which is increasing in prevalence. It is known as a syndrome of inadequate insulin action . The type 1 condition is insulin dependent. The type 2 condition is non-insulin dependent. Eye, renal, vascular and neurological complications are commonplace.
Definition Diabetes is defined clinically as either a fasting plasma glucose level 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL) or 2-hour plasma glucose 11 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) postprandial
Electronic measurement of capillary blood glucose
Insulitis Insulitis
Metabolic actions of insulin in striated muscle, adipose tissue and liver
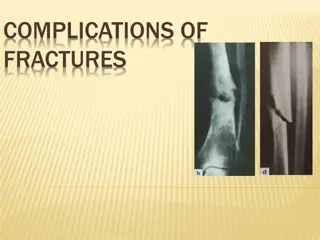
Complications of Diabetes Atheroma Hypertension Diabetic nephropathy Diabetic retinopathy Bacterial infection Peripheral neuropathy
Nodular glomerulosclerosis in a person with long-standing diabetes
Nephrosclerosis in a person with long- standing diabetes