PCR Purification with SPRI Method
Learn about the importance of purifying PCR products using the Solid-Phase Reversible Immobilization (SPRI) method to remove impurities and concentrate target DNA for sensitive processes like sequencing by nanopore. Explore the principles, goals, components removed, and steps involved in this purification technique.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Purification of PCR products by SPRI
What is a PCR (summary)? Polymerase Chain Reaction -> to copy DNA Reaction attempt Buffer DNA-Template DNA- Polymerase dNTPs PCR Steps: Denaturation Annealing Elongation Polymerase extends DNA only in 5 -3 direction DNA is made of 2 strands DNA which joinied by complementary base pairing
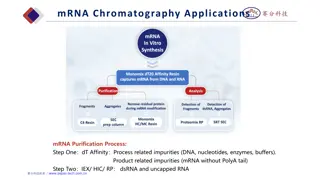
Why is purification of the PCR Product needed? Sequencing by nanopore is a highly sensitive process Components that are contained after PCR: DNA-Polymerase (clogs the pore of Nanopore) Primer Nucleotides (unwanted dNTPs could lead to false sequencing results) DNA-Template Target DNA Purpose of purification: Remove the impurities Concentrate the target DNA
SPRI (Solid-Phase-Reversible-Immobilization) Goal: purify the PCR product to gain only our wished Gene ( 1500 BP) What does it remove? DNA-Polymerase Primer DNA-Template Nucleotide
Principle SPRI (Solid-Phase-Reversible-Immobilization) Is based on the negative load of the DNA and positive loaded beads which bind the DNA Magnetic Beads Relies on a magnetic fields by attracting negative loaded DNA
Selective Binding The biding depends on the size of the fragment because of a special polymer coating Reversible Immobilization Binds under binding condition -> can be released under elution condition
2. Separate DNA on the beads using a magnet 2.1. washing with ethyl alcohol 3x


![[PDF⚡READ❤ONLINE] The International Space Station: Building for the Future (Spri](/thumb/21686/pdf-read-online-the-international-space-station-building-for-the-future-spri.jpg)