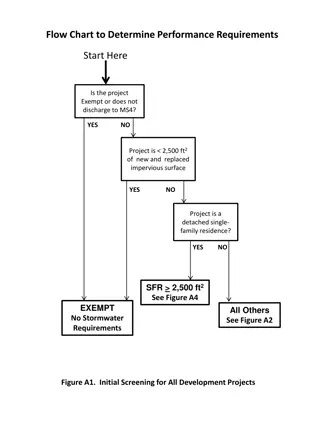
Performance Requirements Flow Chart
A detailed flow chart outlining the performance requirements based on different project criteria such as impervious surface area, project type, and special circumstances. It guides developers on the stormwater requirements to be met, including site design, water quality treatment, runoff retention, and peak management for various development projects. The chart helps in determining the specific performance requirements for each project category.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Intervention Intervention Mapping Step 3: Mapping Step 3: Program Design Program Design
Intervention Mapping Steps 1. Logic model of the problem 2. Program outcomes and objectives (logic model of change) 3. Program design 4. Program production 5. Program implementation plan 6. Evaluation plan 2
Step 3: Tasks 1.Generate program themes, components, scope, and sequence 2.Choose theory- and evidence-based change methods 3.Select or design practical applications to deliver change methods 3
Intervention Logic Model INSERT Figure 6.2 HERE Figure 6.1 4
Task 1: Generate Program Themes, Components, Scope, and Sequence The product of the first part of Step 3 is an initial plan that describes the program Dismiss all preconceived notions and program constraints What would we do if we could do anything that comes to mind? 5
Program Themes A theme is a general organizing construct for a program Some programs have several subthemes Either can be related to the Behavioral or environmental change objectives Priority population Program content
Theme Based on Health Behavior and Priority Population Reprinted with permission from the National Center for Farmworker Health
Designing Program Components Scope and sequence Breadth and amount of program Order in which components are delivered Setting & duration Delivery vehicles Messages Creativity 8
Scope and Sequence for TLL Temple Foundation Stroke Project INSERT Table 6.1 HERE Table 6.1 9
Communication Channels and Delivery Vehicles Interpersonal Communication Channels Volunteers, peer leaders, teachers, health care providers, community health workers (promotoras) Mediated Communication Channels Circulating print: Local and online newspapers, magazines, newsletters, e-mail blasts Display print: Billboards, posters, brochures, flip charts Radio: News items, interviews, PSAs Television: News stories, talk shows, interviews, edutainment, PSAs, infomercials, novellas Videotape: training, documentary, role model stories Computer & internet-based: decision-support, curricula, serious games, simulations, websites Phones & smart phones: text messages, apps Social media: Facebook, twitter, emerging social networks
Task 2: Choose Theory- and Evidence-based Change Methods A method is a general process for influencing changes in the determinants of behavior and environmental conditions An application is a practical technique for the operationalizing methods in ways that fit with the intervention group and the context in which the intervention will be conducted 11
Selecting Methods Different methods are effective for influencing different determinants Select appropriate methods for all change objectives in your behavioral and environmental matrices Pay attention to the parameters for use for each selected methods Method Modeling Parameters for use Attention, remembrance, reinforcement of model, identification with model, coping model instead of mastery model 12
Core Processes for Selecting Methods Organize complete list of change objectives by determinants (the matrix columns) Formulate questions about methods Brainstorm provisional list of methods that may influence each determinant Topic approach: Go to the literature related to the specific problem to identify evidence to support, refute, or add to list of methods Construct approach: Review the list of methods, determinants, and objectives, and follow these constructs to theories General theories approach: Review the list of methods for general theoretical patterns Consider the need to collect additional data on methods through qualitative/quantitative research
Task 3: Select or Design Practical Applications to Deliver Change Methods Select or design practical applications to operationalize change methods One change method may be accomplished by many applications - decide which applications best fit the situation s context 14
Example Methods and Applications from the TLL Temple Foundation Stroke Project INSERT Table 6.19 HERE Table 6.19 15
Test Your Methods & Applications IQ Modeling Persuasion Guided practice Reattribution Role model stories Support groups Reinforcement Certificate of achievement Social comparison Fear arousal Patient counseling Stimulus control No-smoking signs Video presentation of learner attempts at skill Coping response planning
Example It s Your Game Keep It Real (IYG) A sexual health education program for middle school students 17
Task 1: Generate Program Themes, Components, Scope, and Sequence Setting Urban middle schools Duration 12 lessons in 7th & 8th grade Delivery Vehicles Classroom lessons (interpersonal) Role plays, group discussion Journaling Parent-child homework Computer activities (technology) Selected activities tailored by gender, sexual experience Parent newsletters (print materials) 18
Scope & Sequence 7th Grade 8th Grade Lesson Lesson Topic Delivery Lesson Lesson Topic Delivery 1 Pre-Game Show Classroom 1 Pre-Game Show Classroom 2 & 3 Healthy Friendships Classroom Computer 2 Consequences of Pregnancy Classroom 3 & 4 Consequences of STI/HIV Pregnancy Computer Classroom 4 & 5 Setting Personal Limits & Detecting Risky Situations (general) Classroom Computer 5 Condoms & contraception Computer 6 & 7 Refusal Skills (general) Classroom 6 & 7 Setting Personal Limits & Detecting Risky Situations (about sex) Classroom Computer 8 Know your Body Computer 8 & 9 Healthy Relationships Computer 9 Setting Personal Limits (about sex) Classroom 10 Refusal Skills (about sex) Classroom 10 & 11 Refusal Skills (about sex) Classroom Computer 11 Computer Free Time Computer 12 Post Game Show Classroom 12 Post Game Show Classroom
Theme: Its Your Game, Keep It Real Game = Life Real = Telling it like it is, being respectful, being responsible, doing the right thing, being yourself, being healthy and happy How do you keep your game real? Respecting yourself and respecting others Playing by your rules
Additional Subtheme Select your personal rules ahead of time Detect signs or situations that could challenge your rules (risky situations) Protect your rules Avoid risky situations ahead of time Refusal skills and alternative actions
Tasks 2 & 3: Choose Theory- and Evidence- based Methods and Practical Applications Determinants Example Methods Information Transfer Anticipated Regret Modeling Guided Practice with Feedback Example Applications Knowledge Quizzes & games about puberty, sex, reproduction, condoms Attitudes Journal Activity (My #1 reason not to have sex is .because if I have sex ) Skills & Self- efficacy Role Plays Identifying & avoiding risky situations Using refusal skills Demonstrations Correct condom use Modeling Normative Beliefs Peer Video Other students saying they ve chosen not to have sex Older teens saying they use condoms Parent role model stories 22
Summary IM Step 3 comprises 3 key tasks: 1. Generate program themes, components, scope, and sequence 2. Choose theory- and evidence-based change methods 3. Select or design practical applications to deliver change methods