Pharmacodynamic Profile of PL-ASA vs. Enteric-coated Aspirin at 81 mg Dose
Comparison study on the pharmacodynamic effects of PL-ASA, a novel phospholipid-aspirin complex liquid formulation, and enteric-coated aspirin at an 81 mg dose. Explores faster absorption and bioavailability benefits of PL-ASA over enteric-coated aspirin.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pharmacodynamic Profile of PL-ASA, a Novel Phospholipid-Aspirin Complex Liquid Formulation, Compared to Enteric-coated Aspirin at an 81 mg Dose Results from a Prospective, Randomized, Crossover Study Franchi F, Schneider DJ, Prats J, Fan W, Rollini F, Been L, Taatjes-Sommer HS, Deliargyris EN, Angiolillo DJ TCT 2021
Background Immediate release (IR) aspirin (IR-ASA) is associated with risk of mucosal damage in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Enteric coated aspirin (EC-ASA) was designed to reduce GI injury by bypassing the stomach and releasing ASA in the duodenum and is today the standard of care in secondary prevention. However, evidence shows that EC-ASA results in greater variability in absorption and antiplatelet effect than IR-ASA. PL-ASA (VAZALORE, PLx Pharma Inc.), a novel FDA-approved, liquid-filled phospholipid- ASA capsule, is an IR formulation, designed to release aspirin in the duodenum, thus limiting GI injury, while still providing fast and complete drug absorption and potent and reliable COX-1 inhibition. Previous studies have compared the 325-mg dose of PL-ASA to IR-ASA and EC- ASA; this study is the first to investigate the pharmacokinetics (PK) of the 81-mg dose of PL- ASA. We also sought to assess the early pharmacodynamic (PD) effects of PL-ASA compared to EC-ASA Franchi F et al TCT 2021
Methods This is a randomized, open-label, crossover study assessing PK and PD after a single 81- mg dose of PL-ASA vs. EC-ASA under fasting conditions in 36 subjects between 18 and 75 years of age. Subjects were randomly assigned 1:1 to either PL-ASA followed by EC-ASA or EC-ASA followed by PL-ASA with a 14-day washout period between the two study drugs. PK parameters for acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid were obtained. PD assessments included the comparison between PL-ASA and EC-ASA for platelet aggregation following arachidonic acid (AA) and collagen stimuli, and measurement of thromboxane B2 (TxB2) Franchi F et al TCT 2021
Demographic Results 36 subjects were randomized and completed the study mean age: 48.8 years (range: 22 - 69) females: 26 (72.2%) race: 26 white, 6 black mean BMI: 34.5 kg/m2 Franchi F et al TCT 2021
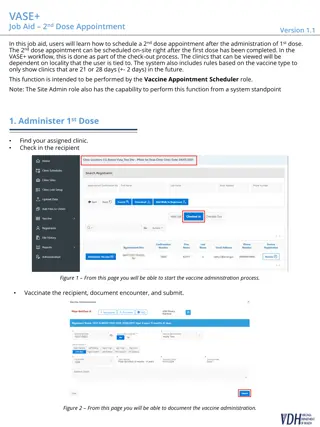
Pharmacokinetic Profile PL-ASA Provides Faster Absorption and More Complete Bioavailability vs. EC Aspirin Plasma concentrations over time (mean, n=36) Acetylsalicylic Acid Salicylic Acid 500 4000 Mean plasma concentration (ng/mL) Mean plasma concentration (ng/mL) 400 3000 PL-ASA 81 mg EC-ASA 81 mg PL-ASA 81 mg EC-ASA 81 mg 300 2000 200 1000 100 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Time (hr) Time (hr) Franchi F et al TCT 2021 Acetylsalicylic Acid
PK Parameters EC ASA PL-ASA P-valuea Acetylsalicylic acid (N=34) (N=23) 367.86 416.13 720.10 600.73 <0.0001 0.001 <0.0001 Cmax (ng/mL) AUC0-t (hr*ng/mL) Tmax (hr) 4.00 (1.50, 6.63) 1.01 (0.47, 3.03) Salicylic acid (N=36) (N=36) 2940.93 13123.96 4.89 (2.00, 11.9) 4095.24 14848.45 1.52 (0.55, 5.92) <0.0001 0.02 <0.0001 Cmax (ng/mL) AUC0-t (hr*ng/mL) Tmax (hr) Cmax and AUC are presented as geometric least-square mean; Tmax is presented as median (minimum, maximum). a: All p-values were calculated by using mixed-effect, repeated measure ANOVA model with sequence, period, and treatment as fixed effects, and subject as random effect. Franchi F et al TCT 2021
Pharmacodynamic Profile: LTA Arachidonic Acid-Induced Light Transmission Aggregometry (LTA) over Time (median, n=36) PL-ASA Provides Faster and Stronger Platelet Inhibition with Lower Levels of AA- induced Platelet Aggregation vs. EC-ASA 100 Median % aggregation (maximum) PL-ASA 81 mg EC-ASA 81 mg 80 P<0.0001 P=0.0022 60 P=0.0002 40 P=0.0075 20 P=0.0509 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Time (hr) Franchi F et al TCT 2021
Conclusions PK Profile: PL-ASA, a novel phospholipid-aspirin formulation in a liquid-filled capsule that has been shown to be bioequivalent to IR-ASA, results in faster and more complete absorption after a single 81 mg dose compared to EC-ASA. PD Profile: In arachidonic acid-induced platelet aggregation, as assessed by light transmission aggregometry, PL-ASA provides more potent and earlier inhibition of platelet aggregation compared to EC-ASA. Assessments of TxB2 (data not shown) were consistent with LTA results. The observations of the current study are consistent with previous findings from published comparative studies with the 325 mg dose.1,2 PL-ASA is a novel aspirin formulation that provides more predictable PK and PD effects compared with enteric- coated aspirin. 1Angiolillo et al, J Thromb Thrombolysis 2019;48:554 62 2Bhatt DL, Grosser T, Dong J et al JACC Franchi F et al TCT 2021