Phase Change Materials Experiment
This experiment focuses on testing a mix of Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate and Calcium Chloride Hexahydrate as Phase Change Materials (PCM) for Thermal Energy Storage (TES). The setup includes ABS pipes, copper tubes, thermocouples, and data acquisition tools to analyze the energy generated during the phase change process. Dr. Wade's data on material properties, including melting profiles and latent heat, are utilized for the experiment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1 ME476C Prototype II Aaron Espinoza, Maciej Ziomber, Steven Galloway, Janelle Pe a, CourtneyHiatt
2 Prototype Objective 66.6% Calcium Chloride Hexahydrate 33.3% Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate Molecular Weight ? Inlet Temperature(C) Outlet Temperature(C) Temperture Difference: Known: mass(m) Melting Point (C) specific heat(Cp) heat of fusion(F) [kJ/kg] Density (rho) [kg/m^3] Pressure (P) volume(V) Thermal Energy Stored(Q) Change in Internal Energy (U) Specific Enthalpy (h) Phase Change Enthalpy (H) Energy Storage Capacity (ESC) g/mol The main purpose of this experiment is to test Phase Change Materials (PCM) for a future integration into a Thermal Energy Storage (TES) 0 The PhaseChange Material that is being tested is a mix of Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate and Calcium Chloride Hexahydrate 127 1590 Measurements Taken: Temperature Differencebetween the inlet and outletof the fluid to fluid heatexchanger VolumetricFlowRate Energy generated duringthe phase change 0 0 0 0 0
3 ExperimentalDesign & Method Experimental Setup: ABS pipe (2 in diameter, 2 ft long) capped with JB weld and hose clamps 3 Copper tubes (0.5 in diameter, 2 ft long) Tee fittings on ends with barbed fitting for tubing from a hydraulic bench Thermocouples on both ends, spaced by nipples and fittings Mixture: ???2 6?2? + ????2 6?2?
4 Experimental Design & Method Data Acquisition: Pico Data Logger K-Type Threaded Thermocouples Bucket-Timer Test HydraulicBench Graduated Cylinder
5 Data and Results TC Calibration:
6 Data & Results We used a slow bucket-timer flow rates with room temperature water from the hydraulic bench.
7 Data & Results Dr. Wade provided us with data on the properties of the materials: Full melt profile Two melting events
8 Data & Results Q = 2842 uVs * 0.0012656 J/uVs = 3.57 J Qmelt = 3.57 J / .0229 g = 156 J/g (error due to mass loss) - Latent heat
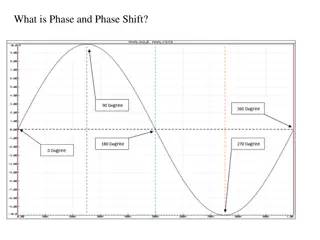
Data & Results Temperature vs. Time Plots: Trial 1: Temperature vs. Time 9 Trial 2: Trial 2: Temperature vs. Time Trial 1: 34 30 Temperature [Deg. C] Temperature [Deg. C] 28 29 26 24 24 22 20 19 18 16 14 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 12.00 14.00 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 Time [Min] 8.00 10.00 12.00 14.00 Time [Min] Ch 7 'Inlet' (C ) Ch 8 'Outlet' (C ) Ch 7 'Inlet' (C ) Ch 8 'Outlet' (C ) Trial 3: Trial 3: Temperature vs. Time 30 Consistently has a difference of approximately 2 C from inlet to outlet as material phase changes Phase change occurrence visible as lines intersect. 28 Temperature [Deg. C] 26 24 22 20 18 16 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 12.00 14.00 16.00 18.00 20.00 Time [Min] Ch 7 'Inlet' (C ) Ch 8 'Outlet' (C )
12 Calculations Error and Uncertainty calculations:
13 Future Work Keep experimental apparatus in thermal equilibrium by capping ends and filling with room temp water. Running the system with hot and cold water (above and below 22 C) Run hot above 30 C Next semester transition to air flowing through device