Physics Classroom Agenda: Scalar Example, Significant Figures, SI Units
Explore a physics classroom agenda covering topics such as scalar quantities, significant figures, SI units of measurement, and quantitative data. Dive into position-time and velocity-time graphs, learn about precision in measurements, and understand the use of SI prefixes. Get insights into quantitative data and the importance of measurement in science.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
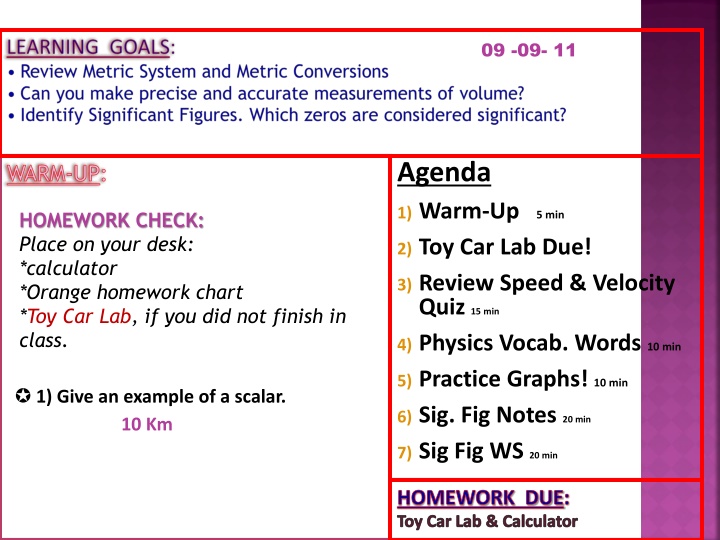
09 -09- 11 Agenda WARM-UP: 1) Warm-Up 5 min HOMEWORK CHECK: Place on your desk: *calculator *Orange homework chart *Toy Car Lab, if you did not finish in class. 2) Toy Car Lab Due! 3) Review Speed & Velocity Quiz 15 min 4) Physics Vocab. Words 10 min 5) Practice Graphs! 10 min 1) Give an example of a scalar. 10 Km 6) Sig. Fig Notes 20 min 7) Sig Fig WS 20 min HOMEWORK DUE: Toy Car Lab & Calculator
VOCABULARY: 1. Position-time graph: graph that shows how position depends on clock reading or time. 2. Slope: ratio of the vertical separation of 2 points on a curve or rise, to the horizontal separation of the points, or run; rise divided by run; change in distance/change in time. 3. Velocity-time graph: plot of velocity of an object as a function of time.
IN SCIENCE Numbers are based on measurement made in the lab. Our data is only as good as the measurements we make and the instruments we use.
QUANTITATIVE DATA Something that has a magnitude size or amount Ex. Length, mass, volume
SI UNITS OF MEASUREMENT One system for all scientists around the world; We must have a standard for comparison length-meter (m) mass- kilogram(kg) time- second (s) volume liter (L)
SI PREFIXES Added to base units to represent large or smaller quantities SI Prefix Unit Abbreviation Factor kilo K hecto h deka da BASE m,g,L deci d centi c milli m Kiss Her Daily Because Divorce Costs Money Exponential 103 102 101 100 10-1 10-2 10-3
EXAMPLE 10 g = ____________mg? K h da b d c m 10,000
EXAMPLE #2 14.6 dL= __________ kL K h da b d c m 0.00146
SIGNIFICANT FIGURES Shows how PRECISE a measurement is Indicates the QUALITY of the instrument you use (how sensitive or exact) EX. Graduated cylinder vs. beaker
SCIENTIFIC NOTATION Used to write really LARGE or really small # s Why? To save space & time
SCI. NOTATION RULES Written in the form of mX10n m: > or equal to 1 AND <10 EX: 1.0X103
THE STEPS OF THE SCIENTIFIC NOTATION Step 1) Determine the sig figs 106,000,000 Step 2) Determine the value of M using the sig figs 1.06 Step 3) Add the 10 s multiplier 1.06 x 10n
Step 4) Determine the value of n by counting the number of times you move the decimal in the original number to get the value for M Step 5) Determine the sign of n by looking at the direction that you moved the decimal in the original # to get the value or M If you move the decimal to the left in the orginal # n is positive If you move the decimal to the right from the original #, n is negative
CALCULATIONS WITH SIG FIGS Multiplication/Division 1) Multiply/ Divide using original numbers 2) Report answer using the same # of sig figs as the least precise measurement in the problem
RULES FOR ROUNDING -Digit to the right is 5: Round UP -Digit to the right is<5: Round DOWN
ADDITION/SUBTRACTION 1)Add/subtract with original numbers 2)Report answer using the same # of decimal places as the least precise measurement in the problem.
DUE TODAY: Vocab. Chart (KEEP) Sig. Fig Notes (KEEP) Sig. Fig WS The world is the great gymnasium where we come to make ourselves strong. Swami Vivekananda DUE NEXT CLASS: Finish SIG FIG Assignment Binder/folders/CALCULATOR