Plant Adaptations for Water Balance and Gas Exchange
This text discusses the structural and physiological adaptations of xerophytes and halophytes to maintain water balance and facilitate gas exchange. It explains how transpiration and factors like temperature, wind, and humidity impact water loss and gain in plants. The adaptations of halophytes to cope with high salt content in soils are also detailed. Additionally, the effects of water loss on gas exchange, photosynthesis, and plant physiology are explored, along with strategies used by land plants to control water loss and maximize water storage.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
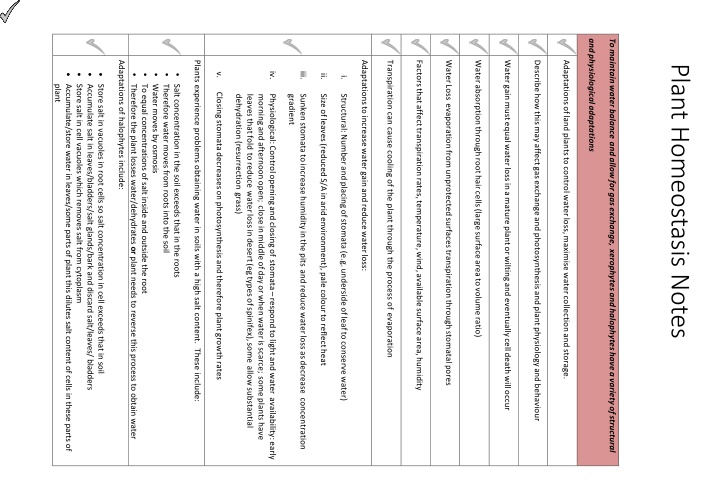
andphysiologicaladaptations Tomaintainwater balanceandallowforgasexchange,xerophytesandhalophyteshaveavarietyofstructural Transpiration can cause cooling of the plant through the process of evaporation Factorsthat affect transpirationrates,temperature,wind,availablesurfacearea,humidity WaterLossevaporationfromunprotectedsurfaces transpiration through stomatal pores Waterabsorptionthroughroot hair cells(largesurfaceareatovolumeratio) Watergainmustequalwaterlossinamatureplantorwiltingand eventuallycelldeathwilloccur Describehowthismayaffectgasexchangeandphotosynthesisandplantphysiologyand behaviour Adaptationsofland plantsto controlwaterloss,maximise watercollectionandstorage. Adaptations of halophytes include: Plants experience problems obtaining water in soils with a high salt content. These include: Adaptationsto increasewater gainandreducewaterloss: Plant Homeostasis Notes iii. iv. v. Accumulate/store water in leaves/some parts of plant this dilutes salt content of cells in these parts of Store salt in cell vacuoles which removes salt from cytoplasm Accumulate salt in leaves/bladders/salt glands/bark and discard salt/leaves/ bladders Store salt in vacuoles in root cells so salt concentration in cell exceeds that in soil Therefore the plant losses water/dehydrates or plant needs to reverse this process to obtain water To equal concentrations of salt inside and outside the root Water moves by osmosis Therefore water moves from roots into the soil Salt concentration in the soil exceeds that in the roots ii. i. plant Closingstomatadecreaseson photosynthesisand thereforeplantgrowthrates Physiological:Controlopeningandclosingofstomata respondtolight andwater availability:early Sunkenstomata toincrease humidityinthe pitsandreduce waterlossasdecrease concentration Size ofleaves(reducedS/Ainaridenvironment), pale colourto reflectheat Structural:Numberandplacingofstomata (e.g.undersideofleaftoconservewater) dehydration(resurrectiongrass) leaves thatfoldtoreducewaterlossindesert(egtypesofspinifex),someallowsubstantial morningandafternoonopen; closeinmiddleofday orwhenwateris scarce;someplants have gradient
Recap: Osmosis & Diffusion Recap: Osmosis & Diffusion Recap: Recap: Plant transport Structures Plant transport Structures
Recap: Transpiration Recap: Transpiration
Topic Question Topic Question 1: 3 & 4) 1: Describe how light, humidity, wind and temperature affect the rate of transpiration (read page 388 Biology WA ATAR Units Light Humidity Factors that increase the rate of transpiration Wind Temperature
Topic Question 2 Topic Question 2: : Describe the environment xerophytes live in and the problems these plants encounter maintain water balance
Topic Question Topic Question 3: 3: Describe adaptations of xerophytes and explain how these adaptations helps the plant to survive in arid conditions Adaptation Type of Adaptation Description of adaptation Explanation of how this adaptation helps the plant to survive in its environment
Topic Question Topic Question 3: 3: Describe adaptations of xerophytes and explain how these adaptations helps the plant to survive in arid conditions Adaptation Type of Adaptation Description of adaptation Explanation of how this adaptation helps the plant to survive in its environment
Topic Question 2 Topic Question 2: : Describe the environment halophytes live in and the problems these plants encounter maintain water balance
Topic Question Topic Question 3: 3: Describe adaptations of halophytes and explain how these adaptations helps the plant to survive in saline conditions Adaptation Type of Adaptation Description of adaptation Explanation of how this adaptation helps the plant to survive in its environment
Topic Question Topic Question 3: 3: Describe adaptations of halophytes and explain how these adaptations helps the plant to survive in saline conditions Adaptation Type of Adaptation Description of adaptation Explanation of how this adaptation helps the plant to survive in its environment






















