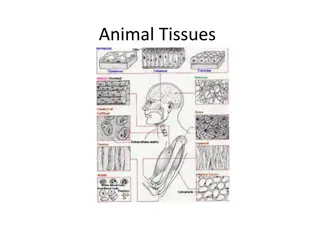
Plant and Animal Tissues
A comprehensive overview of plant and animal tissues, including their structures, functions, and differences. Learn about the specialized roles of various tissues in both plants and animals, such as meristematic tissue, xylem, phloem, muscles, and more. Understand how tissues in plants and animals support growth, movement, and energy requirements.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Year 3: Animals including Humans Knowledge Mat: Is chocolate good for us? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about Animals including Humans nutrition Nutrition involves drinking enough water and eating the right amount of items from the four main food groups. All animals need water, air and food to survive. The different ways in which humans can be healthy. Examples of healthy and unhealthy food choices The parts of the human body and what they do. All animals need water, air and food to survive. The different ways in which humans can be healthy. skeleton The human skeleton is made of bone and grows as we grow. Our skull protects our brain and our ribs protect our heart and lungs. What are the different food types? Fruit and vegetables Bread, rice, potatoes, pasta and other starchy foods. Milk and dairy Oils and spreads Meat, fish, eggs, beans and other non-dairy sources of protein. muscles Muscles are attached to bones by tendons and help them to move. When a muscle contracts it gets shorter and pulls on the bone it is attached to. diet Our bodies need a balanced diet to work properly. This involves drinking enough water and eating healthily. joint Joints allow the body to make movements. The body has many bones and are connected through the joints. Investigate pelvis The pelvis is a bony cradle-shaped structure located at the base of the spine. Match animals to their skeletons and explain your reasons for this. Explore ideas about what would happen if humans did not have skeletons. Create a presentation to show how muscles contract and relax. Compare the size of straight arms and bent arms. Measure around the top of an arm when it is straight and when it is bent . What do you notice? cartilage Cartilage is a connective tissue found in many areas of the body including joints between bones e.g. the elbows, knees and ankles. What are the different types of nutrients? Protein- help your body to grow and repair itself Carbohydrates -give you energy Fats - give you energy Vitamins -keep your body healthy Minerals- keep your body healthy Fibre - helps you to digest the food that you have eaten Water -helps to move nutrients in your body and get rid of waste that you don t need rib cage It is made up of curved bones. The rib cage is found in the chest area. It protects a person s internal organs from damage. tendon Muscles are attached to the bone by tendons and work in pairs to allow for smooth movement. spine Also known as your backbone, your spine is a strong, flexible column of ring-like bones that runs from your skull to your pelvis.
Year 3: Rocks Knowledge Mat: What is beneath my feet? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about our rocks. fossil Soil contains nutrients and these help plants to grow. The meaning of the word absorb. Why some materials are used for certain purposes because of their properties A fossil is the preserved remains or traces of a dead organism. soil Soil consists of a mix of organic material (decayed plants and animals) and broken bits of rocks and minerals. What are the different types of rocks? There are three types of rocks that are formed naturally. Igneous: When molten magma cools, igneous rocks are formed. Sedimentary: Sometimes, little pieces of rocks that have been weathered can be found at the bottom of lakes, seas and rivers This is called sediment. Metamorphic: When some igneous and sedimentary rocks are heated and squeezed (pressured), they form metamorphic rocks. crystals Crystals are a special kind of solid material where the molecules fit together in a repeating pattern. sedimentary Sedimentary rocks are made when sand, mud and pebbles get laid down in layers. Over time, these layers are squashed under more and more layers. metamorphic When a rock experiences heat and pressure, it becomes a metamorphic rock. All metamorphic rocks start as another type of rock. Investigate igneous Igneous rock is formed when magma cools and solidifies. It may do this above or below the Earth's surface. Explore the types of rocks you can find in the local environment. Explain why rocks are used for different purposes based on their properties. Research the different living things whose fossils are found. Explore the different kinds of soils , including those you can find in the local environment. What are fossils? Fossils are the remains of prehistoric life. They are usually formed when a living thing (plant or animal) dies and the body is covered up or buried by sediment over tens of thousands of years. decaying Gradually being destroyed by a natural process. organic matter Organic matter is matter that has come from a recently living organism. It is capable of decaying. What is soil? Soil is made from pieces of rock, minerals, decaying plants and water. When rock is broken down into small grains, soil is formed. Permeable Is substance is permeable, something such as water or gas can pass through it or soak into it.
Year 3: Light Knowledge Mat: Do shadows change? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about light. reflection Certain things produce light, usually by burning (e.g. the Sun) or electricity (e.g. street lights) Shiny materials do not make light but do reflect it. Shadows are caused when certain materials block light A reflection occurs when a ray of light hits a surface and bounces off. How are shadows formed? When light is blocked by an opaque object, a dark shadow is formed. An opaque material blocks light so we can t see through it and shine a light through it. shadows A shadow is formed when an object blocks out the light. The object must be opaque or translucent to make a shadow. light source The main light source for Earth is the Sun. Some other luminous objects give out light, for example, torches, candles and lamps. opaque Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through them, in most cases creating a shadow. Translucent If a material is translucent, some light can pass through it. Investigate When light is shone onto a transparent object, the light travels through it, we can see through it and it makes a very faint shadow. light is shone onto a translucent object, some of the light travels through it, we can see bright light sources through it and it makes a fairly dark shadow Transparent The brightness of torches - can you put torches in order from brightest to dimmest? What would make it a fair test? Why do lights seem brighter in the dark? How can you change the size and shape of shadows by using the same object? If an object or substance is transparent, you can see through it When dim light that is not bright emits to emit a sound or light means to produce it bright a colour that is strong and noticeable, and not dark The size of a shadow changes as the light source moves. The further away the light source is, the smaller the shadow is. The closer the source of the light, the bigger the shadow. Dark The absence of light
Year 3: Plants Knowledge Mat: Do plants have legs? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about plants roots What do different plants need to grow? air water Sunlight nutrients from the soil room to grow suitable temperature The root is the part of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. Which things are living and which are not. A variety of common wild and garden plants, including deciduous and evergreen trees and how to identify them. The structure of common flowering plants. Seeds and bulbs grow into mature plants Plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy. Plants and animals depend on each other to survive. stem The stem is the plant axis that bears buds and shoots with leaves. nutrients Nutrients are the food the plant wants. Most of the plant s nutrients comes from the soil. What are the functions of the different parts of a flowering plant? The petals on a flower are usually bright - this is to attract bees and other insects so that they can collect pollen to make seeds. The seeds are then able to grow to make new plants. This is called germination. Leaves use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make food for the plant. The stem carries water and other nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. Leaves use this water to make food. The stem also helps to keep the plant upright so that the sunlight can reach it easier. The roots help to anchor the plant in the soil. They also absorb water and nutrients from the soil for the stem to carry to the rest of the plant. Absorb soak up or take in Investigate seed dispersal Compare the effect of different factors in plant growth (e.g. the amount of water, the amount of light). Discuss what would make this a fair test. Place white carnations in dyed water to observe how plants transport water Seed dispersal is the movement or transport of seeds away from the parent plant. Pollination To pollinate a plant or tree means to fertilise it with pollen. This is often done by insects seed formation A seed is a small baby plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. stigma The stigma is usually sticky and receives pollen. How is water transported within plants? Water is absorbed from the soil by the roots. It is then transported from the roots to the stem and then to the rest of the plant. anther The stamen has a pollen producing structure at the end which is called the anther.
Year 3: Forces and Magnets: Do Opposites attract? Subject Specific Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Sticky Knowledge about forces and magnets Attract What is a force? Forces are pushes and pulls. These forces change the motion of an object. They will make it start to move or speed up, slow it down or even make it stop If one object attracts another object, it causes the second object to move towards it The shape of some materials can be changed when they are stretched, twisted, bent and squashed. Know how different toys move. Know what a force is and be able to explain that a push and pull are types of forces. That when forces are applied to an object they allow them to move or stop moving. The strength of the force determines how far and fast an object moves. Force the pulling or pushing effect that something has on something else Magnet How do forces work? Forces act in opposite directions to each other a piece of iron or other material which attracts magnetic materials towards it Magnetic field How do magnets work? Magnets produce an area of force around them called a magnetic field. When objects enter this magnetic field, they will be attracted to or repelled from the magnet if they are magnetic. When magnets repel, the push each other away When magnets attract, they pull together. If you place two magnets so the south pole of one faces the north pole of the other, the magnets will move towards each other. This is called attraction an area around a magnet, or something functioning as a magnet, in which the magnet s power to attract things is felt Investigate Investigate the amount of friction created by different surfaces. Use measures (such as length and time) to show how far or fast and object travels. Compare how different things move and group them. Observe how a magnetic field attracts iron filings by using a bar magnet. Non-magnetic an object that is not magnetic Opposite Opposite is used to describe things of the same kind which are completely different in a particular way. For example, north and south are opposite directions Repel When a magnetic pole repels another magnetic pole, it gives out a force that pushes the other pole away Resistance a force which slows down a moving object or vehicle