Plant Life Cycle and Growth Processes Explained
Explore the fascinating world of plants through visuals and descriptions. Learn about the essential elements plants need to grow well, the process of germination, photosynthesis, flowering, pollination, fertilization, and seed dispersal. Discover the intricate stages of a plant's life cycle, from seed to mature plant, and understand the importance of sunlight, air, water, warmth, and minerals in plant growth. Uncover the secrets of how plants move towards light, reproduce through fruits and seeds, make their own food, and undergo growth from seedlings to larger plants.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
4 Living Processes Movement- towards light Reproduction- fruits and seeds Nutrition- plants make their own food Growth- seedlings to bigger plants
What do plants need to grow well? Sunlight Air Water Warmth Minerals http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/scienceclips/ages/7_8/plants_ grow.shtml
Growing plant Life Cycle of a Plant Flowering plant j0283845 Germination Pollination Dispersal of seeds Fertilisation
Germination When a seed starts to grow Warmth Air Water Root down shoot up Grow leaves (to find light) (begin making food)
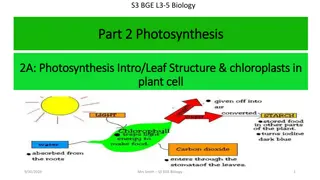
Photosynthesis Making food using sunlight Carbon Dioxide Food and Oxygen Chlorophyll in LEAVES IN OUT and Light
Flowers Attract insects with their sticky nectar and bright colours Male part- STAMEN (Anther and filament) Female part- CARPEL (Stigma, style and ovary)
Pollination The transfer of pollen onto the stigma Two ways: Insect- pollen sticks to the insect and is transferred to the female part (stigma). Wind- pollen is blown onto the stigma.
Fertilisation Joining of the pollen and the egg to make a seed. Pollen (male sex cell) travels along the style to reach the carpel where the female eggs are stored. The fertilised egg becomes a seed.
Dispersal of Seeds Seeds are carried away from the parent plant to stop overcrowding 3 ways: By wind- dandelion seeds are blown away. By animals- they eat berries the seeds come out in the poo! By explosion- seed pods dry up then burst.