Positive Behaviour Support Framework
Positive Behaviour Support (PBS) framework aims to assess challenging behavior, develop personalized support plans, and enhance quality of life outcomes. By understanding the role of environment, PBS combines person-centered values with science to implement proactive and reactive strategies. Active Support complements PBS by promoting participation in meaningful activities to foster independence and inclusion regardless of intellectual disability or challenging behavior.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
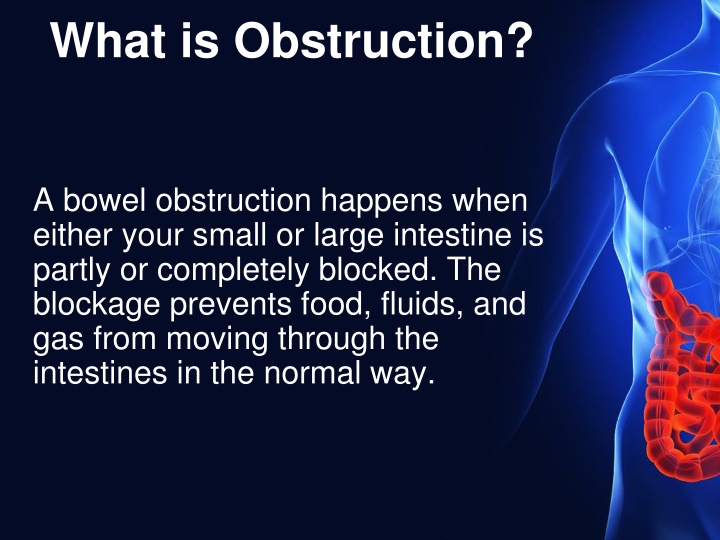
What is Obstruction? A bowel obstruction happens when either your small or large intestine is partly or completely blocked. The blockage prevents food, fluids, and gas from moving through the intestines in the normal way.
Causes of Obstruction Adhesions/ Scar Tissue (most common cause) Small bowel tumors Tumors from nearby organs e.g.. Pancreas Gallstones Hernias Inflammatory changes Crohn's disease (can twist or narrow the intestine)
Symptoms Cramping and belly pain that comes and goes. The pain can occur around or below the belly button Vomiting Bloating and a large, hard belly Constipation and a lack of gas, if the intestine is completely blocked Diarrhoea, if the intestine is partly blocked
Diagnosis An abdominal X-ray, which can find blockages in the small and large intestines. A CT scan of the belly, which helps your doctor see whether the blockage is partial or complete.
How is it treated? Most bowel obstructions are partial blockages that get better on their own A doctor may place a tiny tube called a nasogastric (NG) tube through your nose and down into your stomach which aids in relieving pain by removing gas and fluids. Surgery is almost always needed when the intestine is completely blocked or when the blood supply is cut off. A colostomy or an ileostomy may be needed.